Donald Bowersox, a long-time business professor at Michigan State University and one of the progenitors of modern supply chain management, once said, “The job of supply chain is clearly a senior management challenge, and it’s one that sits right alongside the other C-level jobs in the corporation. We may call it something different going forward, but basically it will remain the stewardship of moving products from the material origin points all the way through the process of conversion to the end consumers efficiently, effectively, and relevantly. That challenge is a big one and will continue to be for a long time. So I don’t see a next organizational evolution. Instead, I see the supply chain manager becoming more deeply involved in the corporate strategic initiatives and being part of the C-team management.”
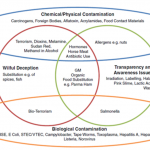
Applying this approach to food safety in the supply chain has become more critical during the last few years as a result of regulatory, market and consumer pressures. At the start of this century, only 15 years ago, the food safety director rarely, if ever, interacted with the CEO. Many retailers didn’t even have such a position, or it was combined with quality control or loss prevention.
Now, not only does the top food safety manager have the ear of the CEO, he or she is engaged with all senior executives. Part of this is the result of the Food Safety Modernization Act, which holds those officers personally liable for a wide variety of preventable incidents. Likely bigger causes for the shift are the changing market and the changing consumer, which both relate directly to the company’s brand reputation. And in the food business, everything starts and stops with the supply chain.
Why? Because the supply chain is ground zero for the failures that are responsible for causing food safety problems. And the supply chain is where food safety problems are prevented. It is the choke point or series of choke points that allow or prevent spoiled and tainted product from getting to the consumer. It is also the process by which that unsaleable product is reclaimed so as to ensure it never enters the marketplace.
It is critical for the food safety manager to work closely with the merchandisers and the store operations teams, as they have the relationships with suppliers and work to ensure that standards for everything from ingredients to production are met with every shipment. But it’s even more critical for those professionals to work closely with the supply chain team to determine weak links in the system and address those pressure points before they cause real damage. Without food safety-supply chain collaboration, the risks to a company’s reputation multiply. With it, the likelihood of a food safety incident reaching consumers diminishes tremendously.
It’s becoming clearer every day—if you don’t button up your supply chain, somebody else, namely the government or the consumer, will and the results won’t be pleasant.