The beverage industry is undergoing a period of technological transformation. As consumer demand and supply chain pressures reveal the shortcomings of older systems and processes, beverage manufacturers are embracing new technologies at an unprecedented pace. While many of these trends are promising, some are more impactful than others. With that in mind, here are the five technologies making the biggest impact in the beverage industry.
Automation
While automation isn’t necessarily new, it is reaching new heights. Automation is becoming an essential part of the beverage sector as robotic systems become more accessible and versatile, and talent becomes harder to acquire.
The food and beverage industry currently has more than 4 million open positions and could add another 370,000 by 2031. With fewer young workers entering manufacturing, beverage facilities are turning to robotics to sustain productivity. The more automated a facility is, the more it can accomplish despite having fewer employees, offsetting the labor shortage.
Automation applies to more than just physical workflows, too. Robotic process automation is seeing increased adoption in back offices, where it can be used to boost productivity and reduce errors.
Artificial Intelligence
Another impactful technology in the beverage sector is artificial intelligence (AI). As beverage workflows become increasingly digitized, they generate more data. AI algorithms can analyze that data to turn it into actionable insights, helping beverage manufacturers predict and adapt to incoming changes and optimize their operations.
Common industry thinking holds that companies can only optimize two of three key variables—time, cost and quality—simultaneously. However, it’s often difficult for humans to determine which is the most valuable area for improvement in their businesses. AI can analyze workflow data to reveal weak points and highlight changes that would have the most significant impact, helping leaders make these decisions.
AI can also help predict future changes, including shifting consumer demand. With this insight, beverage producers can adjust to minimize losses and capitalize early on new trends. Those that don’t embrace AI analytics may quickly fall behind the competition as this technology becomes increasingly common.
The Internet of Things
As AI adoption grows, the Internet of Things (IoT) can help beverage companies make the most of these algorithms. IoT devices give previously unconnected machines wireless connectivity, providing more data points for AI models to analyze, improving their accuracy. This connectivity and data collection can also improve transparency.
One of the most impactful use cases for IoT sensors is in the supply chain. Connected tracking devices can provide real-time updates on shipment locations, temperature, vibrations and other factors. If anything falls out of acceptable parameters or schedules, they can alert relevant stakeholders so they can adapt to ensure safe, timely shipments.
IoT devices can also improve machine health by alerting workers to needed repairs. This data-driven, need-based approach prevents costly breakdowns while minimizing downtime from unnecessary maintenance.
Biotechnology
While many of the most impactful technologies in the beverage industry appear within manufacturing facilities, some focus on earlier workflows. Biotechnology, such as gene editing, can optimize the farming operations that produce the ingredients beverage companies need.
Some bioengineered crops require less water to grow or are pest-resistant, minimizing the need for pesticides. These upgrades reduce farms’ ongoing expenses, making beverage ingredients cheaper for production facilities. Other bioengineering processes can make certain ingredients healthier or less environmentally impactful, both of which appeal to consumers.
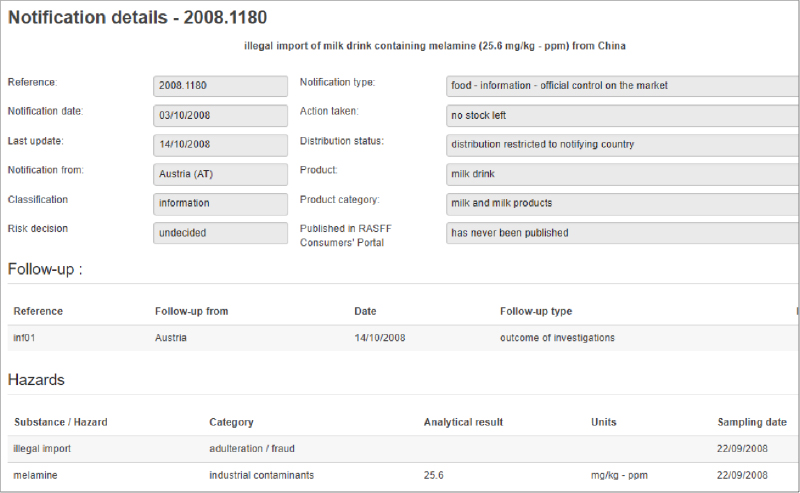
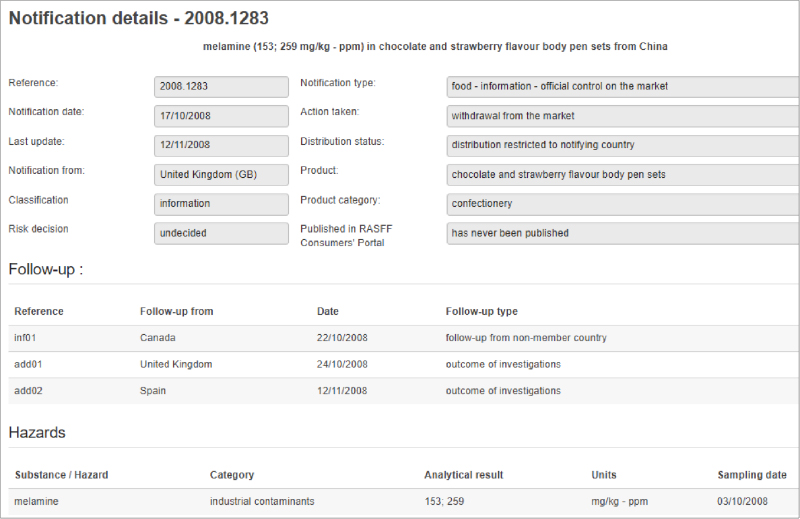
Emerging biotechnology solutions let beverage companies use specially designed enzymes to gauge milk contamination and spoilage better. With these biological markers, businesses can ensure they don’t send poor-quality products to market and can trace contamination issues, leading to long-term improvements.
Renewable Energy
Another increasingly impactful technology for beverage companies today is renewable energy. As climate issues become more prominent, consumer preferences lean towards sustainable companies and products, even if that means paying more for products. Switching to renewable power helps energy-hungry beverage factories adapt to this demand and protect the environment.
Because renewables such as solar and wind are technologies, not fuel sources, they will only become cheaper and more efficient over time. Consequently, switching to these technologies is becoming an increasingly viable option for companies. They can also reduce energy costs long-term, as facilities begin to generate their own power instead of buying it from the grid.
Additionally, growing climate urgency may lead to increased regulations around industrial energy sources. Shifting to renewable power now can ensure beverage companies minimize disruption from any changing legislation.
Virtually every industry today is undergoing a tech-driven transformation. Capitalizing on this movement means being able to separate the buzzwords from the technologies that hold the most promise. These five technologies are among the most impactful for beverage companies today. As their adoption grows, they could dramatically alter the face of the industry.