“A new era of smarter food safety is coming,” said Frank Yiannas, FDA’s deputy commissioner of food policy and response, at the GFSI Conference 2019 in Nice, France. He went on to explain, “a smarter food safety is people-led, FSMA-based and technology-enabled.” Afterwards, Yiannas announced the need for a greater budget for the FDA to invest in modern food safety for 2020 and beyond.
Now the question is, when this new era comes, are you ready?
The food industry is relatively behind on technology compared to other industries, or even within our daily lives. Take a look at the cell phone you have now compared to what you had 10 years ago; it has come a long way with all of its handy and useful features. Why can’t the food industry also benefit from technology? Of course, every coin has two sides, but no one would deny that technology played a significant role in bringing the world closer and making it more efficient nowadays.
The scary part of change is that it’s hard to predict what and when they will come to us, however, they also force us think outside of the box. Instead of debating whether incorporating advanced technology into our daily operations makes sense, why don’t we take a look at our current processes in place and see where technology can truly help us? We now have the opportunity to take advantage of technology to enhance our food safety and quality culture at our own facility. Here are some thoughts to share.
1. Identify what can be automated in your current process with technology
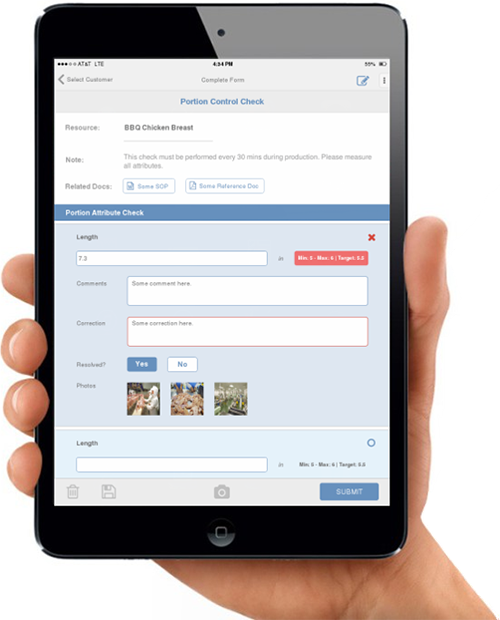
Certain things just can’t be replaced by technology, such as risk assessment or hazard identification (at least for now). However, inventory, temperature checking, testing results recording, or anything executing a command from you or implementing a part of your SOPs can potentially be automated. Execution is also the part where the most error could occur, and technology can help improve accuracy and consistency. Identify those steps systematically and understand what data needs to be captured to help your food safety management system.
2. Work with your technology developer to build technical requirements
Explain to the technology developer exactly how you want the program to operate daily. List the operating steps along with responsibilities step-by-step, and identify what requirements are needed for each step. Translating the paper SOP to a computer program plays an important role in this transition. Not only does it set the foundation for your future daily operation, but it also ensures that the control parameter is not lost during the transition.
3. Keep the integrity of the food safety management system through verification and validation
Once processing steps are done by technology, it doesn’t mean that we no longer have to do anything. We need to verify and validate the technology with certain frequency to ensure the steps are controlled as intended. Confirming that the software or system is capturing the right data at the right time becomes key to ensure the integrity of control risks is not compromised.
4. Utilize “preventative maintenance” on all technology used on site
Just like all equipment, food safety technology needs a preventive maintenance schedule. Check whether it is properly functioning on a certain frequency based on the safety impact in your process flow and take actions proactively.
5. Learn from your own records
The time saved from traditional ways allows us to have more time for looking at control points and records received to identify areas for continuous improvement. There are many ways of studying the data with modeling and trend analysis based on your own facility situation. Either way, those records are your own supporting documents of any changes or modifications to your food safety management system, as well as strong support to your risk assessment for justifications.
Just like Yiannas said, a smarter food safety system is still FSMA based. The goal has never changed; we want to produce sustainable, safe and high-quality products to our consumers, whether we use traditional or advanced approaches. After all, we are utilizing technology as a modern way to help us enhance and simplify our food safety management system; the outcome from the automated technology is still controlled by us.
So when the era comes, we all want to be ready for it.