Beer is one of the world’s oldest beverages, with evidence suggesting production as far back as the Bronze age. While beer is no longer used as renumeration for work as it was in the Mesopotamian Fertile Crescent, it is nevertheless a common pleasure for many people. Craft brewing is a relatively new phenomenon, and quite different from the brewing processes of antiquity. In the United States, immigrants from Germany and Czechia began to experiment with new recipes for craft beer in the 1960s. These recipes, often based on the Bavarian 16th century Reinheitsgebot, or purity laws, ensured that only the purest, highest quality ingredients went in to make beer: Water, barley, hops and yeast.
Since then, there has been a rapid growth in the number of microbreweries that experiment with “new-world” hops and grains to create huge ranges of flavorful beers that go far beyond traditional recipes. This variety in brewing ingredients and approaches has, in part, supported the explosion of a mass market for craft beer. In 2020, the global market value of craft beer was estimated at nearly $165 billion, and is expected to grow to nearly $554 Billion by 2027, with the largest growing markets in countries like China, Japan and the United States. There has also been a shift in which types of beers are consumed, with more premium or specialized craft beers increasing in market share with respect to low-cost mass-production beers.
In such a crowded and dynamic market, beer producers are faced with competitive challenges like never before. Ensuring a consistently high-quality product with a distinctive flavor profile that can be enjoyed time and time again is critical for market success. One of the key challenges standing in the way of achieving this is turbidity, or “haze”, in the end product. Such haze can give an unsightly first impression to consumers, compromise flavor, and negatively impacts shelf stability. In this article we discuss how new, advanced turbidity testing technologies are enabling brewers to quickly and efficiently eliminate haze from their beers, supporting breweries in their goals of delivering great consumer experiences again and again.
Quality over Quantity
With the growing “premiumization” of beers, ever-greater attention and importance is being placed on interesting and consistent flavor profiles. Often, this includes beers made from ingredients far outside the relatively strict Reinheitsgebot recipe, including additions such as coffee, fruit and spices. The emphasis on more complex flavor profiles is pushing beer tasting to be taken as seriously as wine tasting, with perfectly balanced beers often being designed to match certain foods.
However, the addition of these newer ingredients can introduce challenges into the brewing process, especially as they can be sources of turbidity-causing impurities that may affect the quality, flavor and shelf stability of the final product. This is particularly challenging when beer brewing is scaled up to larger manufacturing quotas, where careful control of variables like ingredient choices, recipes and manufacturing methods are critical for ensuring the consistency and quality of the beer from batch to batch.
To meet these needs, modern breweries are increasingly using new and advanced technologies throughout the brewing process to maintain high quality products. Technologies like water purification systems, titrators and portable instruments such as hand-held pH meters and spectrophotometers are all being utilized to improve and refine the manufacturing process. A major focus of this technological drive is in turbidity detection and removal.
What Is Haze, and Where Does It Come From?
Haze is a broad term referring to evenly distributed turbidity—suspended, insoluble material which can appear in the final product. Haze can be divided into several types, most commonly: Chill haze, a temporary haze that disappears when a chilled beer warms to room temperature; and permanent haze, which is present at all temperatures. Haze can also be divided into biological haze (caused by microbiological growth in the beer) and non-biological haze (caused by a wide variety of non-living material, such as peptides, polyphenols and starches).

Since turbidity can be the result of unwanted microbes, wild yeast or protein particles, these deposits, although not unsafe to consume, can significantly alter the flavor profile of the beer, adding unpleasant acidity, sourness, or even “off” flavors. Bacteria are one of the major sources of turbidity in beers, particularly lactic acid-producing bacteria (LAB), such as Lactobacillus. While small amounts of lactic acid can add pleasant, desirable sour flavors in sour beers, the over-presence of these bacteria can be a major cause of contamination, so their levels must be closely monitored in the brewing process. Other bacteria like Pectinatus species can also “infect” beers, causing turbidity as well as “off” aromas and flavors due to the creation of hydrogen sulfide and fatty acids.
Importantly, turbidity-causing compounds can collect in the product from all stages of the brewing process:
- This starts with the source of water, and how it is filtered and treated. For example, a high presence of calcium in brewing water can cause precipitation of calcium oxalate.
- Mashing, the first stage of the brewing process, produces a malt extract from mixing grains and water. The malt extract is a liquid containing sugar extracted during mashes and has high viscosity and high protein content. At this stage fungi (like Penecillium), wild yeasts (Candida) and bacteria can all enter the mix to cause turbidity later on.
- From there, the process of lautering separates the wort from the grain. The wort is then boiled with hops, clarified, then fermented with yeast. The fermentation process is a common step when turbidity-causing bacteria like Lactobacillus and Pediococcus can contaminate the mixture.
- The fermented beer product is then stored for anything from three weeks to three months in a storage tank where a second fermentation takes place. Then it is filtered and packaged into barrels, bottles, or cans; all of which are also potential sources of turbidity-causing bacteria like Pectinatus.
The filtration and pasteurization processes are key for removing sources of turbidity. However, these processes do not necessarily remove all sources of turbidity, especially if aspects of the brewing process are altered by external factors (e.g., subtle shifts in the mashing temperatures) and cause a buildup of contaminants that is too great to filter out. Therefore, effectively monitoring and minimizing turbidity throughout the brewing process is critical, allowing brewers to make timely corrective adjustments, reducing a buildup of contaminants in the final product.
Advanced Methods for Turbidity Testing
To support effective haze removal and ensure beer consistency, turbidity measurements must be taken throughout the entire brewing process. Measurements should therefore be quick and efficient, and able to measure large quantities of beer in a short space of time, especially in high-production breweries. As such, advanced on-site turbidity testing technologies that are efficient and easy to use are ideal, and can rapidly streamline quality control in the brewing process. For example, with turbidity meters, breweries can swiftly check that their fining or filtration process is yielding a desired end product, and if an issue arises during the clarification process, an onsite turbidity measurement can pick this up right away for speedy corrective action. Such speedy rectification minimizes the chances of ruined batches and resultant profit loss to the brewery.
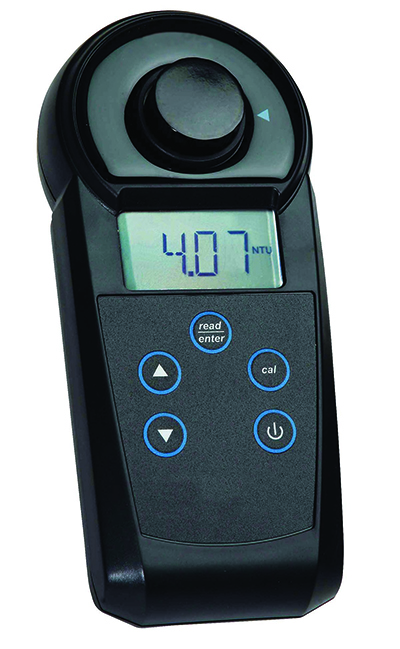

Modern turbidity meters work by using an infrared LED light source to measure light scattering in a solution. These handy devices allow brewers to perform rapid testing of beer with simple grab samples, meaning samples can be analyzed without having to disturb the brewing process. The LED light sources used in more advanced meters also have several benefits. For example, the LED does not require a warm-up period like older tungsten lamps, meaning it is ready to use at all times. Secondly, infrared LED light sources prevent color interference, which is especially useful for testing darker beers. Finally, the LED will last the life of the meter and give stable signals, meaning that calibration does not drift. Turbidity meters can also test for chill haze, allowing brewers to check for problems that can cause the beer to turn cloudy during prolonged chilling.
Quality Kings
Quality control of the brewing process is crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of beer products that keep customers returning time and time again to their beers of choice. In a hyper-competitive market, brewers must use all the advantages they can to stay ahead of the game. Hazy beers can be particularly off-putting to customers if they are expecting bright, clear products, and critical qualities like taste and aroma can be very unpleasant if contamination isn’t carefully controlled. Moreover, unwanted turbidity in beers can negatively impact shelf stability, with resultant impact on profitability and brand reputation.
Owing to the complexity of beer making, the sources of turbidity are multiple, meaning that careful testing of turbidity is critical. In helping to overcome these challenges, advanced turbidity meters are enabling brewers to perform efficient and simple measurements on-site throughout the brewing process. This is helping to drive more timely tweaks to the brewing, filtration and storage steps to ensure consistent, high-quality beers with carefully crafted flavor profiles reach the market.