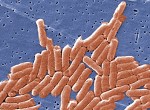
The USDA has finalized federal standards to lower the incidence of Salmonella and Campylobacter in ground chicken and poultry (including raw chicken breasts, legs and wings, which comprise about 80% of the chicken that American’s purchase). FSIS updated its microbial testing schedule at poultry facilities and will also start posting food safety performance about companies online.
“This approach to poultry inspection is based on science, supported by strong data, and will truly improve public health,” said USDA Deputy Under Secretary for Food Safety Al Almanza in an agency press release. “The new performance standards will complement the many other proactive, prevention-based food policies that we’ve put in place in recent years to make America’s supply of meat and poultry safer to eat.”
Intended to achieve at least a 30% reduction in Salmonella illnesses, a pathogen reduction performance standard for chicken parts, ground chicken and ground turkey is being finalized by FSIS. It is doing the same to achieve a 32% reduction in illnesses from Campylobacter in chicken parts and ground chicken. FSIS estimates a low prevalence of Campylobacter in ground turkey and is thus aiming for a 19% reduction.
“Over the past seven years, USDA has put in place tighter and more strategic food safety measures than ever before for meat and poultry products. We have made strides in modernizing every aspect of food safety inspection, from company record keeping, to labeling requirements, to the way we perform testing in our labs,” said Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack in the release. “These new standards, in combination with greater transparency about poultry companies’ food safety performance and better testing procedures, will help prevent tens of thousands of foodborne illnesses every year, reaching our Healthy People 2020 goals.”