The FDA issued the first of several final regulations aimed at modernizing the food safety system through the use of hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls. Inherent in this system are a number of requirements that eligible food facilities must follow, such as developing a written food safety plan, monitoring, corrective actions and verification. Laboratory testing is an essential component as well.
Robin Stombler presented “Laboratory Oversight and FSMA: Why and When” at the Food Labs Conference in Atlanta, GA | March 7–8, 2016So, what should food facilities know about laboratory testing within the context of the preventive controls for human food final rule? First and foremost, the final rule states, “facilities have a responsibility to choose testing laboratories that will produce reliable and accurate test results.” While a future regulation is expected to address the need for accredited laboratories and model laboratory standards, the preventive controls rule adopts other requirements pertaining to testing. Here are five questions that food facilities should ask about testing and the preventive controls rule.
1. What is the difference between pathogens and microorganisms?
The final rule defines “pathogen” to mean a microorganism that is of public health significance. A microorganism is defined as “yeasts, molds, bacteria, viruses, protozoa and microscopic parasites, and includes species that are pathogens.” Microorganisms that are of public health significance and subject food to decomposition or indicate that the food is adulterated or is contaminated with filth are considered “undesirable.”
2. How must food facilities account for pathogens?
Food facilities must prepare and implement a written food safety plan. One component of the food safety plan must include a written hazard analysis. This analysis must identify known or reasonably foreseeable hazards. These hazards may be biological, which includes parasites, environmental pathogens and other pathogens.
In another example, the food safety plan must include written verification procedures. This is to demonstrate that the facility is verifying that its preventive controls are implemented consistently and are significantly minimizing or preventing the hazards. These verification procedures are intended to be appropriate to the particular food facility, the food in question, and the nature of the preventive control and its role within the facility’s food safety system. With this in mind, facilities must conduct activities such as product testing for a pathogen or an appropriate indicator organism or other hazard, and environmental monitoring.
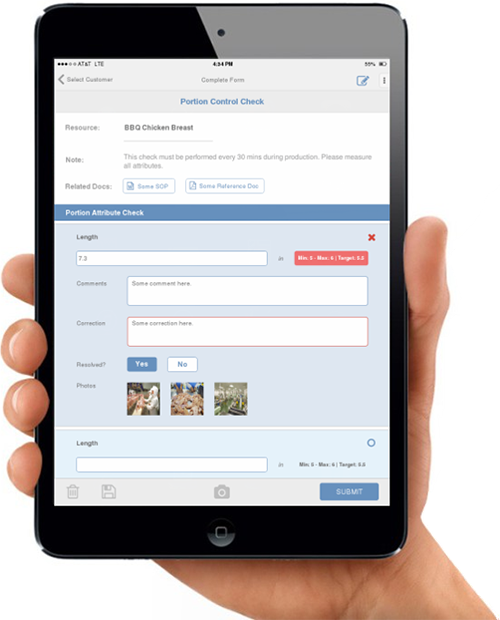
3. Are there written procedures specific to product testing?
Yes. Procedures for product testing must be scientifically valid and must identify the test microorganisms or other analytes. The procedures for identifying samples, including their relationship to specific lots of products, must be written and implemented. The procedures for sampling, including the number of samples and the sampling frequency, must be outlined. The facility must recognize the laboratory conducting the testing as well as describe the tests that are performed and the analytical methods used. Corrective action steps must also be included.
4. What are the procedures for environmental monitoring?
Similar to product testing, these procedures must be scientifically valid, identify the test microorganisms, and be put in writing. For routine environmental monitoring, the location from which the samples are collected and the number of sites that are tested must be stated. The final rule indicates that the “number and location of sampling sites must be adequate to determine whether preventive controls are effective.” Written procedures must also identify the timing and frequency for collecting and testing samples. Again, similar to product testing, the laboratory conducting the testing and the tests and analytical methods used must be divulged. Corrective action procedures must also be included.
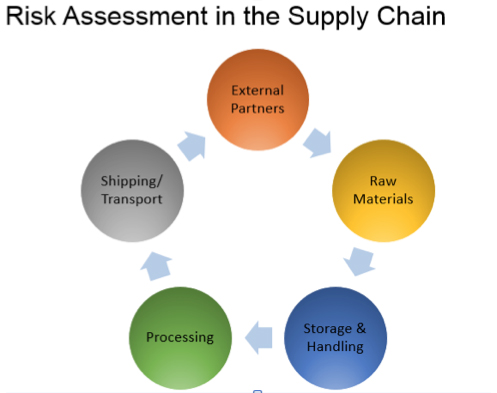
5. How does the supply-chain program incorporate testing?
A receiving facility is required to document a written supply chain program in its records. A component of that program includes documentation of sampling and testing performed as a supplier verification activity. The documentation must include identification of the raw material or other ingredient (including, if appropriate, lot number) and the number of samples tested. It also means that the tests conducted and the analytical methods used must be identified. The date the test is conducted as well as the date of the test report must be provided, and the identity of the laboratory performing the testing must be revealed. Any corrective actions that were taken in response to a hazard detection must also be reported.
This Q&A provides a glimpse into how the preventive controls final rule for human food incorporates laboratory testing. For more details, access the final rule.