High-profile food recalls and food-borne illnesses continue to keep food safety top of mind. Yet, many in the industry are still struggling to put the best practices we’ve learned over the years about how to properly secure our global food chain into practice. Put simply: The focus needs to be on prevention rather than reaction.
Food safety procedures must be strengthened across the board to meet increasing regulatory pressures and prevent massive recalls and illness outbreaks. FSMA puts the principles of prevention into law. The first major update of federal food safety laws since 1938, it was signed into law by President Obama at the start of 2011. After years of debate, it is now finalized and implementation can begin. The objective of FSMA is to ensure that the U.S. food supply is safe by shifting the focus from reaction to prevention. Now, who can argue with that?
FSMA also pushes the FDA to extend beyond its traditional reactive role. For the first time, the FDA has the power to stop unsafe and possibly contaminated food from entering the food supply.
Let’s take a quick step back so we can explore how to best put it into action. FSMA is made up of five primary provisions:
- Preventive controls
- Inspection and compliance
- Imported food safety
- Response
- Enhanced partnerships
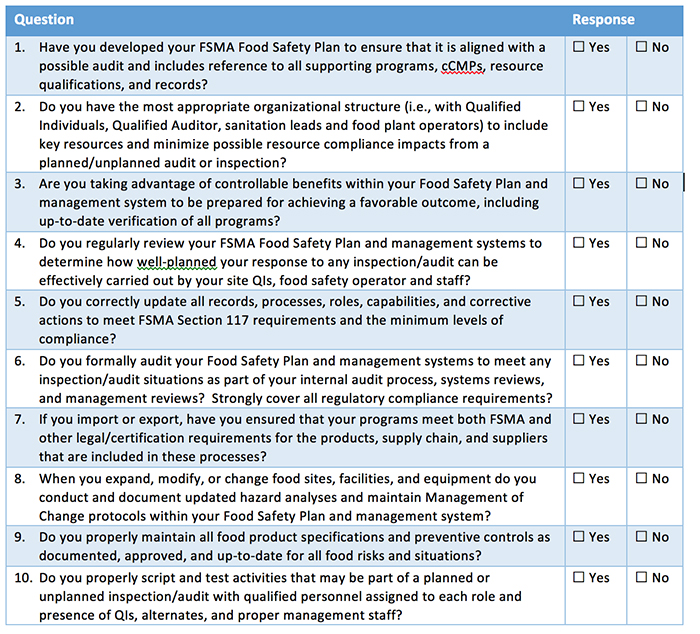
I’d argue that the first provision is the true heart of FSMA: Prevention. The first provision focuses on preventative controls and provides a framework for an effective food safety program. In FSMA, this is broken into five key parts, including hazard analysis, preventative controls, monitoring, corrective action and verification. But what does that mean to you? You can best comply with these requirements by implementing better visualization, documentation and communication tools. Let’s walk through each section and the types of tools that you should consider.
Hazard Analysis. Most companies have strong HACCP plans in place, taking account food safety hazards at all stages of production. Risk assessment and risk management must be taken into account and critical control points defined. However, to manage this going forward, consider tools that enable visibility into the current and historical situation at those control points to allow your team to see their proximity to each other, as well as to other components in the plant.
Preventive Controls. Preventative controls are also called out as part of the FSMA requirements. This includes food allergen, supply-chain and sanitation controls in place, as well as sound recall plans. Again, critical control points (CCPs) are the key to ensuring your controls are effective. Also, consider trying indicator test points to stay one step ahead! Indicator test points, as advocated by food safety leader, John Butts, are one or more steps removed from your CCPs. By testing in these areas, you can identify possible risk areas before they even reach control points. This enables a much more proactive approach.
Monitoring. Your plant should have a monitoring plan that includes written procedures for monitoring preventive controls and how frequently they should be performed. This plan should take into account zone coverage, randomization, test frequency, test timing and sampling order. Depending on the business and regulatory rules of a plant, testing should include non-food contact and food contact surfaces. In order to ensure that testing is representative of the conditions in the plant, randomization of test points is important. In addition, test frequency and test timing should be defined, and organizations should seek tools that help to automate these business rules.
Corrective Action. Hope for the best, but always plan for the worst. What is your corrective action plan? You must have a written procedure for identifying and correcting a problem. For both your plant and for regulators, a clear record of your plan and that the steps were followed to close out any issues is required. Make sure that the team understands the steps that are required, number of re-tests and any recall requirements. Look for tools that automatically alert the relevant team members of the situation and track response and testing so that you can easily share this level of detail as needed.
Verification. Trust but verify. Having a plan is only half the job. Using your environmental and finished product testing programs to ensure that controls and corrective actions are effective turns your plan into action. Rapid testing technologies keep the time between testing and results tight. Also, communication of verification results keeps the team coordinated around food safety.
The move to more preventative food safety procedures does not have to create massive headaches. Compliance with FSMA will ultimately help your business and guarantee that you are providing safe food for your customers to consume. Many food companies have been implementing these best-practice guidelines for years. Thanks to FMSA, we all now get an easy-to-follow checklist.
Shifting from reaction to prevention makes food safer—and now, it is also the law. The first step is to make sure you have a good understanding of the components. Only then can you find the best tools and technologies to support you. Lastly, make sure that your team is well aligned around the goals and objectives of your food safety program. Together, we can make food safer.