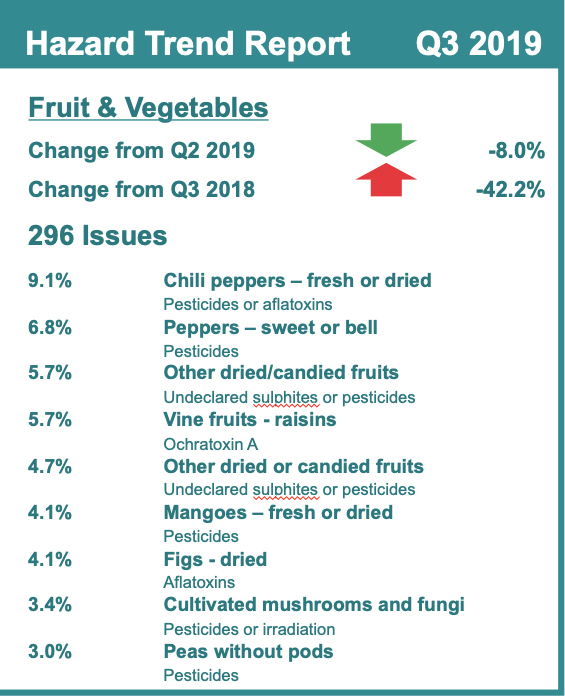
When it comes to addressing food safety, did the industry really make any progress in 2018? In 2019, what new approaches or technologies can be successfully applied to prevent problems before they occur and minimize the consumer risk, minimize the market impact, and speed up the identification, isolation and recall of contaminated products?
Field-packed produce offers a unique challenge to the fresh food supply chain, as it is not processed and is not required to adhere to an FDA mandated HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) process. It has been a challenge for field-packed produce suppliers to proactively identify or prevent contaminated produce from entering the supply chain. As a result, during serious contamination incidents, the reaction is to pull and destroy all suspect product from store shelves and supply chain. Due to the lack of data isolating the source of the contamination, this is the safest approach, but it’s costing the industry millions of dollars. Ultimately, our inability to prevent or quickly isolate these events causes confusion among consumers who don’t know who to trust or what is safe to eat, resulting in a prolonged market impact.
In response to the latest E. coli outbreak involving romaine lettuce, the industry has proposed a voluntary item-level label that reflects the harvest location and date, to help identify safe product to the consumer. At best, this is a stop-gap solution, as it burdens the consumer to identify safe product.
I work in the fresh produce supply chain industry. When I go to the grocery store, I examine the produce, noting the brand and various other factors. I was aware of the romaine problem and the voluntary labeling program, so I knew what to look for. But I’m an exception. Most consumers don’t know romaine lettuce is grown during the summer and fall in northern California and further south during the winter in regions that include Arizona and Mexico. Most consumers don’t know what the “safe date” for harvest really means—nor should they be required to know this information. They look to the industry to manage this. If we buy a car or microwave oven that is found to be unsafe, the manufacturer and the government are responsible for identifying the problem and recalling the product. Yet, in the produce industry, that responsibility seems to be moving to the retailer and consumer.
It’s an unfair burden, as the retailer and consumer do not have the necessary information to make a definitive judgement regarding food safety. The responsibility needs to be shared across the entire fresh food supply chain. Records about the produce need to be shared and maintained from harvest to retail.
Will 2019 be the year that we realize we can address this challenge proactively to improve the safety of our fresh food?
We need a new approach that leverages innovative technology to provide a more reliable solution. For example, irrigation water is often identified as a culprit in spreading bacteria. Yet even with regular testing of irrigation water, the results do not currently guarantee food safety. We see emerging technology that will make regular testing more reliable, accurate and affordable to facilitate more proactive management of the water supply. This will be a critical part of an overall solution for proactive produce food safety.
Blockchain technology has been hailed as a savior of food safety and traceability. Early in 2018, it was all the rage, as various sources claimed that, by using blockchain, recall times could be cut from days or weeks to seconds. But was this an oversimplification? Perhaps so, as this early hype faded by the middle of the year amidst the various food safety outbreaks that went unresolved. Then last August, Gartner, a market analyst firm, declared that blockchain had moved into the “trough of disillusionment” on its 2018 Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies as a result of over-hyped expectations. The firm predicts that the technology may reach the “plateau of productivity” within the next decade. Can we wait another 10 years before being able to benefit from it? Should we?
We expect that blockchain trials will continue in 2019. But, while blockchain has shown promise in terms of being a secure and immutable data exchange, questions remain. What data about the produce will be entered into the blockchain? How is that data collected? Is the data validated? Bad, inaccurate or incomplete data makes blockchain relatively useless, or worse, as it undermines a trusted platform. Further, without broad agreement and adoption of data collection, blockchain can’t be successful.
For proactive management of food safety, we will also need to address both forward and backward supply chain traceability. One of the challenges realized from recent outbreaks is that it takes time to figure out what is happening. Identifying the source of the illness/outbreak isn’t easy. Once we identify a source (or multiple sources) of the contamination, blockchain—assuming that all of the necessary data has been collected—only helps to more quickly trace back produce to its origin. But, for growers, quickly understanding where all product shipped from a specific location or date is just as critical in understanding and minimizing consumer impact. Tracing product forward enables a grower to proactively inform retailers and restaurants that their product should be recalled.
Blockchain currently does not directly support this forward tracing, but can be augmented to do so. But blockchain can maintain a food safety data item, or items, that could quickly and reliably communicate product status at the pallet-level, providing instant food safety status to the current product owner, even if they didn’t have direct contact with the grower. As such, a hybrid blockchain approach, as espoused by ChainLink Research, is optimal for forward and backward traceability.
Equally important, we need to fully digitize the supply chain to enable blockchain. To make comprehensive data collection feasible, we need to automate data collection by utilizing IoT sensors at the pallet level, to properly reflect how distribution takes place through the supply chain. We need reliable data collection to properly reflect the location and condition of product distributed through a multi-tier distribution network. That level of product data visibility enables proactive management for food safety as well as quality and freshness— well beyond the current trailer-level monitoring that only monitors transit temperatures with no benefit to managing food safety. Effective data capture will define the next generation of fresh food management, as it embraces proactive food safety, quality and freshness management.
Goals for This Year
For 2019, our goals should be to embrace new approaches and technology that:
- Identify food contamination at its source and prevent contaminated food from ever entering the supply chain. We need to focus on developing new technologies that make this feasible and cost effective.
- Accurately and consistently track product condition and authenticity of fresh produce from the time it is harvested until it is delivered. IoT sensors and proactive fresh food supply chain management solutions provide this capability.
- Make it cost-effective and practical for growers, suppliers and grocers to use solutions to improve the entire fresh food supply chain. If we make the process burdensome or without a reasonable ROI, implementation will lag, and the problems will persist. But if we demonstrate that these solutions offer value across the fresh food supply chain—through reduced waste and improved operational efficiency—growers, suppliers, shippers and grocers will embrace them.