Almost everybody loves chocolate, an ancient, basic, almost universal and primal source of pleasure. “The story of chocolate beings with cocoa trees that grew wild in the tropical rainforests of the Amazon basin and other areas in Central and South America for thousands of years… Christopher Columbus is said to have brought the first cocoa beans back to Europe from his fourth visit to the New World” between 1502 and 1504.1
Unfortunately, the production of chocolate and chocolate products today is as complex as any other global food product with supply chains that reach from one end of the world to the other. The complexity of the supply chain and production, along with the universal demand for the finished product, exposes chocolate to increasing pressure from numerous hazards, both unintentional and intentional. For example, we know that more than 70% of cocoa production takes place in West African countries, particularly the Ivory Coast and Ghana. These regions are politically unstable, and production is frequently disrupted by fighting. While production has started to expand into more stable regions, it has not yet become diversified enough to normalize the supply. About 17% of production takes place in the Americas (primarily South America) and 9% from Asia and Oceania.2
In today’s world of global commerce these pressures are not unique to chocolate. Food quality and safety experts should be armed with tools and innovations that can help them examine specific hazards and fraud pertaining to chocolate and chocolate products. In fact, the global nature of the chocolate market, requires fast reflexes that protect brand integrity and dynamic quality processes supported by informed decisions. Digital tools have become a necessity when a fast interpretation of dynamic data is needed. If a food organization is going to effectively protect the public’s health, protect their brand and comply with various governmental regulations and non-governmental standards such as GFSI, horizon scanning, along with the use of food safety intelligent digital tools, needs to be incorporated into food company’s core FSQA program.
This article pulls information from a recent industry report about chocolate products that presents an examination of the specific hazards and fraud pertaining to chocolate and chocolate products along with ways to utilize this information.
Cocoa and chocolate products rely on high quality ingredients and raw materials, strict supplier partnership schemes and conformity to clearly defined quality and safety standards. During the past 10 years there have been a significant number of food safety incidents associated with chocolate products. The presence of Salmonella enterica, Listeria monocytogenes, allergens and foreign materials in cocoa/chocolate products have been reported on a global scale. Today, information on food safety incidents and potential risks is quickly and widely available by way of the internet. However, because the pertinent data is frequently siloed, food safety professionals are unable to take full advantage of it.
Top Emerging Hazards: Chocolate Products (2013-2018)
Publicly available data, from sources such as European Union RASFF, Australian Competition and Consumer Commission, UK Food Standards Agency, FDA, Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ), shows a significant increase in identified food safety incidents for cocoa/chocolate products from 2013 to 2018. For this same time period, the top emerging hazards that were identified for chocolate products were the following:
- Allergens: 51.60%
- Biological: 16.49%
- Foreign bodies: 13.83%
- Chemical: 7.45%
- Fraud: 6.38%
- Food additives & flavorings: 4.26%
- Other hazards: 2.66%
By using such information to identify critical food safety protection trends, which we define to include food safety (unintentional adulteration) and food fraud (intentional adulteration, inclusive of authenticity/intentional misrepresentation) we can better construct our food protection systems to focus on the areas that present the greatest threats to public health, brand protection and compliance.
A Data Driven Approach
Monitoring Incoming Raw Materials
Assessment and identification of potential food protection issues, including food safety and fraud, at the stage of incoming raw materials is of vital importance for food manufacturers. Knowledge of the associated risks and vulnerabilities allows for timely actions and appropriate measures that may ultimately prevent an incident from occurring.
Specifically, the efficient utilization of global food safety and fraud information should allow for:
- Identification of prevalent, increasing and/or emerging risks and vulnerabilities associated with raw materials
- Comparative evaluation of the risk profile for different raw materials’ origins
- Critical evaluation and risk-based selection of raw materials’ suppliers
A comprehensive risk assessment must start with the consideration of the identified food safety incidents of the raw material, which include the inherent characteristics of the raw material. Next, the origin-related risks must be taken into account and then the supplier-related risks must be examined. The full risk assessment is driven by the appropriate food safety data, its analysis and application of risk assessment scientific models on top of the data.
Using food safety intelligent digital tools to analyze almost 400 unique, chocolate product related food safety incidents around the globe provides us with important, useful insights about cocoa as a raw material, as a raw material from a specific origin and as a raw material being provided by specific suppliers. The graph below represents the results of the analysis illustrating the trend of incidents reported between 2002 and 2018. It can be observed that after a significant rise between 2009 and 2010, the number of incidents approximately doubled and remained at that level for the rest of the evaluated period (i.e., from 2010 to 2018), compared to the period from 2002 to 2005.
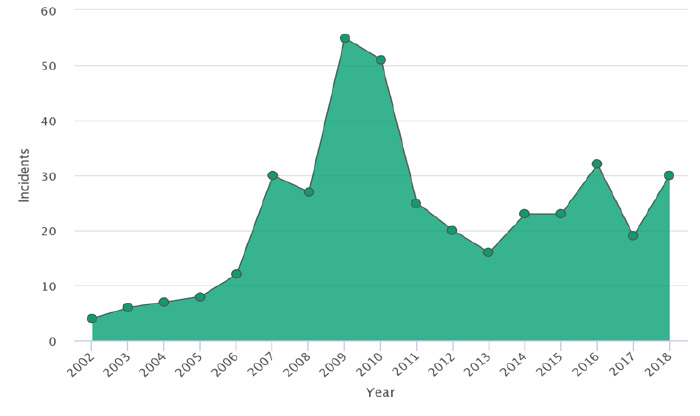
an industry report from FOODAKAI. Used with permission.
By further analyzing the data stemming from the 400 food safety incidents and breaking them down into more defined hazards, for incoming raw materials, we can clearly see that chemical hazards represent the major hazard category for cocoa.
- Chemical: 73.46%
- Biological: 16.49%
- Organoleptic aspects: 5.93%
- Other Hazards: 4.38%
- Fraud: 2.32%
- Foreign bodies: 2.06%
- Food additives and flavorings: .77%
- Allergens: .52%
- Food contact materials: .52%
Using the appropriate analytical tools, someone can drill down into the data and identify the specific incidents within the different hazard categories. For example, within the “chemical hazard” category specific hazards such as organophosphates, neonicotinoids, pyrethroids and organochlorines were identified.
Comparative Evaluation of Risk Profiles for Different Origins of Raw Materials
The main regions of origin for cocoa globally are Africa, Asia and South America. After collecting and analyzing all relevant data from recalls and border rejections and the frequency of pertinent incidents, we can accurately identify the top hazards for cocoa by region.
The top five specific hazards for the regions under discussion are listed in Table I.
| Africa | South America | Asia | |
| 1 | Organophosphate | 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) | 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) |
| 2 | Molds | Pyrethroid | Poor or insufficient controls |
| 3 | Neonicotinoid | Aflatoxin | Aflatoxin |
| 4 | Pyrethroid | Cadmium | Spoilage |
| 5 | Organochlorine | Anilinopyrimidine | Salmonella |
| Table I. Top Five Hazards By Region | |||
After the first level of analysis, a further interpretation of the data using the appropriate data intelligence tools can help to reach to very specific information on the nature of the incidents. This provides additional detail that is helpful in understanding how the regional risk profiles compare. For example, the prevalence of chemical contamination, as either industrial contaminants or pesticides, has been a commonly observed pattern for all three of the regions in Table I. However, beyond the general hazard category level, there are also different trends with regard to specific hazards for the three different regions. One such example is the increased presence of mold in cocoa beans coming from Africa.
The primary hazard categories for cocoa, as a raw ingredient were identified and a comparison among the primary hazards for cocoa by region (origin-specific) should take place. The next step in a data-powered supplier assessment workflow would be to incorporate our use of global food safety data in evaluating the suppliers of the raw materials.
The Role of Global Food Safety Data
This article has been focused on chocolate products but has only touched the surface in terms of the information available in the complete report, which also includes specific information about key raw materials. Let’s also be clear, that the techniques and tools used to generate this information are applicable to all food products and ingredients. As we strive to produce food safely in the 21st Century and beyond, we must adapt our methods or be left behind.
The regulatory environment the food industry must operate in has never been more intense. The threats to an organization’s brand have never been greater. This is not going to change. What must change is the way in which food companies confront these challenges.
Global food safety data can contribute to the establishment of an adaptive food safety/QA process that will provide time savings and improve a quality team’s efficiency and performance.
Based on the continuous analysis of food recalls and rejections by key national and international food authorities, a food safety / quality assurance manager could establish an adaptive supplier verification process and risk assessment process by utilizing the knowledge provided by such data. In that way, QA, procurement, food safety and quality departments can be empowered with critical supplier data that will inform the internal procedures for incoming materials and ingredients (e.g., raw materials, packaging materials) and allow for adaptive laboratory testing routines and compliance protocols. Moreover, food safety systems can become adaptive, enabling quality assurance and safety professionals to quickly update points of critical control when needed, and intervene in important stages of the chocolate manufacturing process.
References
- Discovering Chocolate. The Great Chocolate Discovery. Cadbury website. Retrieved from https://www.cadbury.com.au/About-Chocolate/Discovering-Chocolate.aspx.
- Chocolate Industry Analysis 2020 – Cost & Trends. Retrieved from https://www.franchisehelp.com/industry-reports/chocolate-industry-analysis-2020-cost-trends/.











 The focus of the series is how technology can help FSQA teams execute to meet today’s biggest food safety and quality challenges in program management, compliance, continuous improvement, risk mitigation and much more.
The focus of the series is how technology can help FSQA teams execute to meet today’s biggest food safety and quality challenges in program management, compliance, continuous improvement, risk mitigation and much more.

