Questions were raised recently by brewers and distillers about spent grains being sold as animal feed. FDA recognizes that hazards will be minimal, but charges facilities with protecting spent grains during storage awaiting collection and during transportation as required under FSMA Section 103. This will require protection against physical and chemical contamination and references the inadvertent addition of industrial waste oil to used fryer oil that exposed 100,000 chickens to PCBs. The comment period for this is closed and the final rule is expected to be published this summer. The final rule is scheduled to take effect by August 30, 2015.
Record retention and availability applies to anybody who processes, packs, transports, distributes, receives, holds, and imports human or animal food. However, farms, restaurants, USDA plants, personal consumption, non-food packaging, and food contact packaging manufacturers (but not users of this packaging material) are exempt from this requirement.
The length of record retention depends on the perishability of the food product. If the shelf life is less than 60 days, both the handler and transporter must retain records for 6 months. If the shelf life is between 60 days and 6 months or if the food is animal/pet food, both the handler and transporter must retain records for 12 months. If the shelf life is greater than 6 months, the handler must retain records for 2 years, but the transporter must retain records for only 12 months. Records must be available within 24 hours of a request by FDA and civil action may be taken if records are not kept or made available. This final rule was published on April 4, 2014.
FSMA section updates
These updates are confined to Section 106 — Intentional Adulteration of Foods; Section 111 — Sanitary Transportation of Human and Animal Food; and Section 204 — Designation of High Risk Foods Relative to Record-keeping for Traceability.
To recap, FSMA does not apply to facilities regulated by USDA (meat, poultry, and eggs). Also exempted are juice manufacturers, seafood processors, alcohol-related facilities, low-acid canning (except to expand their hazard analysis), and small businesses.
FDA is considering modified requirements for warehouses and having Preventative Controls only if they are storing refrigerated products.
Section 106 — Intentional Adulteration of Foods
The intent of the proposed rule is for companies to begin using a “qualified individual” to develop a written food defense plan. This plan will protect against intentional adulteration of food for the purpose of causing harm to consumers. The plan should focus on actionable process steps, mitigation strategies, monitoring, corrective actions, and verification.
The regulation exempts very small businesses, companies with a majority of sales to very small businesses, storage facilities (except for bulk liquid storage), alcoholic beverage manufacturers, and animal feed manufacturers and distributors.
Actionable areas and mitigation strategies:
Key actionable areas identified by FDA include: bulk liquid receiving and loading, bulk liquid storage and handling, secondary ingredient handling, and mixing and similar activities. Deliberate acts of contamination may come from acts of terrorism; disgruntled employees, consumers, or competitors; or economically motivated adulteration such as the melamine tainted milk incident.
Companies must identify and implement mitigation strategies, establish procedures to monitor these strategies, implement corrective actions, verify that monitoring is being conducted, train supervisors assigned to actionable process steps, and maintain records.
Examples of mitigation strategies include restricting access to potential adulteration points such as loading and receiving areas, bulk liquids, secondary ingredient handling rooms, and open processing points. Facilities must require tankers to be sealed after loading and the seals must be checked at receiving.
TACCP
FDA is asking for comments on using HACCP principles to develop food defense plans. They are considering calling a control point a TACCP (Threat Assessment Critical Control Point). They are also trying to identify the risk of adulteration to specific processes. Some examples of low risk foods that are hard to adulterate are: shell eggs, whole produce, game meats (not ground), peanuts/tree nuts, and sugar cane/beets. FDA has extended the comment period through June 30, 2014.
Section 111 — Sanitary Transportation of Human and Animal Food
This section builds upon the previously issued Sanitary Food Transportation Act of 2005. It has five major sections: vehicle and transportation equipment, transportation operations, information exchange, training, and records.
The regulation exempts shippers, receivers, and carriers that have less than $500k in total annual sales; the transportation of raw agricultural commodities by farm vehicles; food being shipped through the US to another country; food imported to be exported, but not consumed in the US; shelf stable foods that are completely enclosed in a container; the transportation of compressed gases; and the transportation of live animals.
Vehicles and transportation equipment
The proposed rule will establish requirements for the design and maintenance of vehicles and equipment to ensure that they do not cause contamination of the food being transported. This includes bulk and non-bulk containers, bins, totes, pallets, pumps, fittings, hoses, gaskets, and loading/unloading systems.
The regulation identifies the potential for cross-contamination from: incorrect use of packing materials (reusing wood containers for produce that once held raw meat); using the same hoses or pumps with different allergens or raw and ready-to-eat products; and pallets in poor condition (splintering or projecting nails).
The proposed rule will establish requirements for cleaning, inspection, maintenance, loading/unloading, and operation of transportation equipment to ensure no contamination or temperature abuse of the products during transport. This includes the growth of spoilage bacteria as well as pathogenic bacteria. This will be achieved by ensuring adequate temperature controls, separation of foods with different temperature requirements, and the cleanliness and physical condition of trailers, tankers, pallets, etc.
Communication
Carriers, shippers, and receivers will be required to exchange information regarding prior cargos, the cleaning of bulk transportation equipment, and temperature controls. A log of prior loads must be kept. FDA will not restrict what can be hauled. Rather, they will regulate the cleaning between loads. Wash tickets must be kept and shared with customers. Washing may include sanitizing where necessary.
The carrier must communicate with the shipper and receiver that temperature sensitive foods were transported under the required temperature conditions. This requirement can be waived for short hauls or if the shipper loads a temperature recording device with the shipped products. The shipper and receiver are required to specify in writing the temperature requirements to the carrier. The receiver must confirm compliance.
Training, records and waivers
Carrier personnel must complete training in sanitary transportation practices and must have documentation of this training. This will include personal hygiene for drivers and loading/ unloading workers, training in security, accessibility to hand washing, and avoiding cross contamination in handling mixed loads. Procedures, training, cleaning, prior cargos, and temperature control must be recorded and properly maintained.
Shippers, carriers, and receivers who hold valid permits and are inspected under the National Conference on Interstate Milk Shipments (NCIMS) Grade “A” Milk Safety Program may be waived from these requirements only when they are involved in shipping Grade A milk and milk products. Transportation of food relinquished to consumers may also be waived (such as the pizza delivery guy).
Section 204 — Designating High Risk Foods for the purpose of record keeping related to Traceability
This proposed rule designates high-risk foods based on known food safety risks. The criteria for modeling and scoring risk are:
- Frequency of Outbreaks and Occurrence of Illnesses: This must include chemical and microbiological food safety hazards. Chemical hazards include allergens, mycotoxins, pesticides, and heavy metals.
- Severity of Illness: This will take into account illness duration, hospitalization, and mortality.
- Likelihood of Contamination: This is based on number of recalls and contamination that has been known to occur.
- Pathogenic Growth Potential/Shelf Life: Strong growth potential is likely at temperature at which the food is intended to be held and stored, including refrigeration and room temperature. This will be coupled with shelf life where longer shelf life can increase risk.
- Manufacturing Process Contamination Probability/Intervention: High probability has recurring or frequent detection of contamination. Low probability has infrequent detection of contamination or where contamination is introduced post manufacturing. This will be coupled with the availability and implementation of control measures.
- Consumption: This is the percent of the population that consumes the food.
- Economic impact: Lower is defined as $100-500k impact per year and higher is greater than $10m per year.
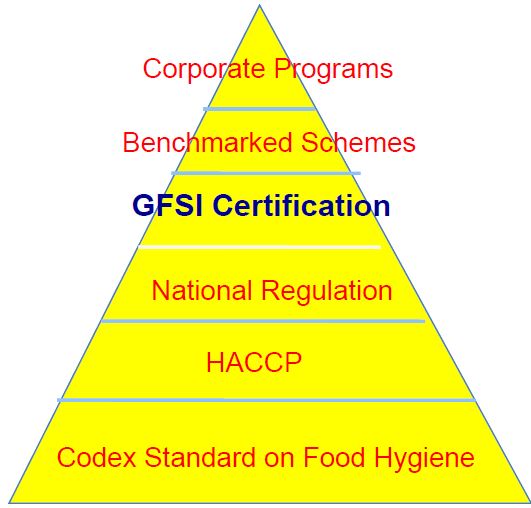
 At the very base of our efforts that are ensconced within these guidance on a sector by sector basis, are the international standards of science based within the Codex Standard on Food Hygiene. On top of that are Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points or HACCP standards. Above HACCP are National Regulations, which includes FSMA in the U.S. and the Safe Food for Canadians Act in Canada. In Europe it’s something different, in Japan it’s something different, but all have iterative levels of science-based regulation in place to ensure the safest control of the food and management of the food. Above National Regulation is GFSI Certification.
At the very base of our efforts that are ensconced within these guidance on a sector by sector basis, are the international standards of science based within the Codex Standard on Food Hygiene. On top of that are Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points or HACCP standards. Above HACCP are National Regulations, which includes FSMA in the U.S. and the Safe Food for Canadians Act in Canada. In Europe it’s something different, in Japan it’s something different, but all have iterative levels of science-based regulation in place to ensure the safest control of the food and management of the food. Above National Regulation is GFSI Certification.

 I recently spoke to a friend who was a plant manager at a food manufacturing company, and he is all too familiar with today’s manufacturing challenges and product quality issues. We discussed how quality processes allow companies to take a more preventative approach to product recalls. He agreed that if quality and regulatory requirements are met before a product leaves the facility, organizations can be sure that they are providing safe product to their customers. The ability to identify issues before a product is distributed can also reduce additional costs associated with product recalls and the impact on a brand’s reputation and sales.
I recently spoke to a friend who was a plant manager at a food manufacturing company, and he is all too familiar with today’s manufacturing challenges and product quality issues. We discussed how quality processes allow companies to take a more preventative approach to product recalls. He agreed that if quality and regulatory requirements are met before a product leaves the facility, organizations can be sure that they are providing safe product to their customers. The ability to identify issues before a product is distributed can also reduce additional costs associated with product recalls and the impact on a brand’s reputation and sales.

