The Golden Age of Bacteriology: Discovering the Unknown in a Farm-to-Market Food Supply.
The last quarter of the 19th Century was both horrific and exciting. The world had just emerged from four decades of epidemic in cholera, typhoid fever and other enteric diseases for which no cause was known. Thus, the great scientific minds of Europe sought to find understanding. Robert Koch integrated Pasteur’s Germ Theory in 1861 with the high technology of the day: Mathematical optics and the first industrialized compound microscopes (Siebert, Leiss, 1877), heterocycle chemistry, high-purity solvents (i.e., formaldehyde), availability of engineered glass suitable as microscope slides and precision-molded parts such as tubes and plates in 1877, and industrialized agar production from seaweed in Japan in 1860. The enduring fruit of Koch’s technology integration tour de force is well known: Dye staining of bacteria for sub-micron microscopy, the invention of 13 cm x 1 cm culture tubes and the invention of the “Petri” dish coupled to agar-enriched culture media. Those technologies not only launched “The Golden Age of Bacteriology” but also guided the entire field of analytical microbiology for two lifetimes, becoming bedrock of 20th Century food safety regulation (the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act in 1938) and well into the 21st century with FSMA.
Learn more about technologies in food safety testing at the Food Labs / Cannabis Labs Conference | June 2–4, 2020 | Register now!Blockchain Microbiology: Managing the Known in an International Food Supply Chain.
If Koch were to reappear in 2020 and were presented with a manual of technical microbiology, he would have little difficulty recognizing the current practice of cell fixation, staining and microscopy, or the SOPs associated with fluid phase enrichment culture and agar plate culture on glass dishes (still named after his lab assistant). The point to be made is that the analytical plate culture technology developed by Koch was game changing then, in the “farm-to-market” supply chain in Koch’s hometown of Berlin. But today, plate culture still takes about 24 to 72 hours for broad class indicator identification and 48 to 96 hours for limited species level identification of common pathogens. In 1880, life was slow and that much time was needed to travel by train from Paris to Berlin. In 2020, that is the time needed to ship food to Berlin from any place on earth. While more rapid tests have been developed such as the ATP assay, they lack the speciation and analytical confidence necessary to provide actionable information to food safety professionals.
It can be argued that leading up to 2020, there has been an significant paradigm shift in the understanding of microbiology (genetics, systems based understanding of microbial function), which can now be coupled to new Third Industrial Age technologies, to make the 2020 international food supply chain safer.
We Are Not in 1880 Anymore: The Time has Come to Move Food Safety Testing into the 21st Century.
Each year, there are more than 48 million illnesses in the United States due to contaminated food.1 These illnesses place a heavy burden on consumers, food manufacturers, healthcare, and other ancillary parties, resulting in more than $75 billion in cost for the United States alone.2 This figure, while seemingly staggering, may increase in future years as reporting continues to increase. For Salmonella related illnesses alone, an estimated 97% of cases go unreported and Listeria monocytogenes is estimated to cause about 1,600 illnesses each year in the United States with more than 1,500 related hospitalizations and 260 related deaths.1,3 As reporting increases, food producers and regulatory bodies will feel an increased need to surveil all aspects of food production, from soil and air, to final product and packaging. The current standards for pathogenic agriculture and environmental testing, culture-based methods, qPCR and ATP assays are not able to meet the rapid, multiplexed and specificity required to meet the current and future demands of the industry.
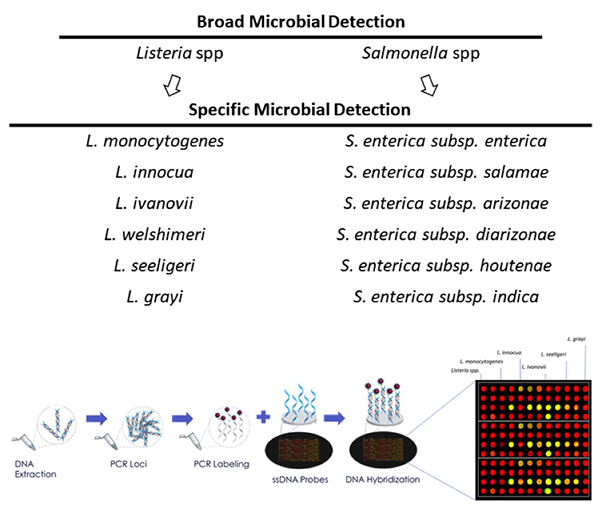
At the DNA level, single cell level by PCR, high throughput sequencing, and microarrays provide the ability to identify multiple microbes in less than 24 hours with high levels of sensitivity and specificity (see Figure 1). With unique sample prep methods that obviate enrichment, DNA extraction and purification, these technologies will continue to rapidly reduce total test turnaround times into the single digit hours while simultaneously reducing the costs per test within the economics window of the food safety testing world. There are still growing pains as the industry begins to accept these new molecular approaches to microbiology such as advanced training, novel technology and integrated software analysis.
It is easy to envision that the digital data obtained from DNA-based microbial testing could become the next generation gold standard as a “system parameter” to the food supply chain. Imagine for instance that at time of shipping of a container, a data vector would be produced (i.e., time stamp out, location out, invoice, Listeria Speciation and/or Serovar discrimination, Salmonella Speciation and/or Serovar discrimination, refer toFigure 1) where the added microbial data would be treated as another important digital attribute of the load. Though it may seem far-fetched, such early prototyping through the CDC and USDA has already begun at sites in the U.S. trucking industry, based on DNA microarray and sequencing based microbial testing.
Given that “Third Industrial Revolution” technology can now be used to make microbial detection fast, digital, internet enabled and culture free, we argue here that molecular testing of the food chain (DNA or protein based) should, as soon as possible, be developed and validated to replace culture based analysis.
References.
- Scallan, E., Hoekstra, R. M., Angulo, F. J., Tauxe, R. V., Widdowson, M. A., Roy, S. L., … Griffin, P. M. (2011). Foodborne illness acquired in the United States–major pathogens. Emerging infectious diseases, 17(1), 7–15. doi:10.3201/eid1701.p11101
- Scharff, Robert. (2012). Economic Burden from Health Losses Due to Foodborne Illness in the United States. Journal of food protection. 75. 123-31. 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-058.
- Mead, P. S., Slutsker, L., Dietz, V., McCaig, L. F., Bresee, J. S., Shapiro, C., … Tauxe, R. V. (1999). Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerging infectious diseases, 5(5), 607–625. doi:10.3201/eid0505.990502





