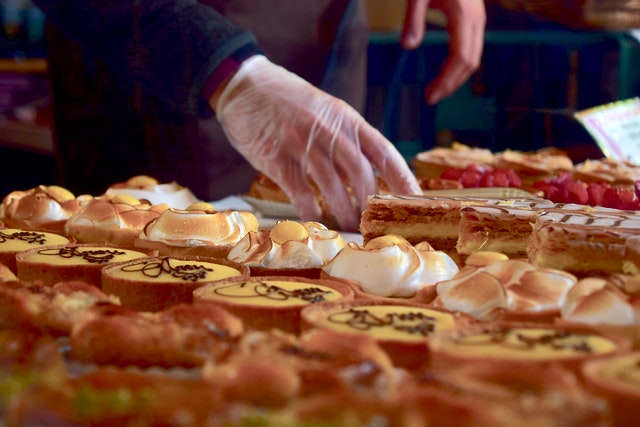
Every company that grows, produces, packs, processes, distributes and serves food has a food safety culture. In the food industry, when looking at food safety culture there are essentially two groups: The correction and the prevention groups. Basically, the prevention group is constantly improving their food safety practices to minimize foodborne illness while the correction group waits until there is an outbreak to make changes.
The correction group isn’t proactive and has a number of excuses that keep them from implementing a food safety program. Oftentimes owners or managers think, “The chances of my company being involved in a food safety outbreak are so rare, I just won’t worry about it.” Or they think, “The cost of having a food safety program is so prohibitive that I’d rather handle the consequences of an outbreak if it were to arise.” Also, sometimes there’s a lack of knowledge and some producers don’t even know about food safety programs and don’t have or want to take the time to learn about them.
If your food company is in the corrective group, you are not alone. Three years ago a private study was done to see how many food facilities could pass a basic Good Agriculture Practice (GAP) and/or Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) audit. It was discovered that less than 20% of these companies would be able to pass the most basic food safety audit. This number is staggering and unfortunately the correction group is much larger than anyone thinks—it equals a majority of the facilities at around 80% of the food industry. This statistic is frightening and needs to be addressed to help reduce outbreaks.
What does the preventative group look like? Well it is more of an investment up front, but in the end helps reduce risk and costs. Companies that take on this responsibility go through an audit and implement procedures that prevent outbreaks. That is level one. The next level of protection involves applying and gaining a certification. All of these procedures help to give your organization a barrier against costs such as crisis management with a PR firm, a recall that leads to lost product and sales, and a thorough clean-up process.
Food safety prevention is an ongoing journey of understanding your many risks and implementing procedures and processes to minimize these risks. Prevention is not a one person job, but rather the whole company needs to join the common cause of protecting the brand and more importantly customers lives.
The cost though is always a huge consideration and can become a deterrent to implementation. Oftentimes owners or managers of facilities will say, “The cost of food safety prevention is so prohibitive that we can’t implement a program.” Yes, there is a cost to building, implementing, and maintaining a preventative food safety program. However, this cost pales in comparison to a corrective program.
Overall Cost of Correction: FDA – Lives – Individual Companies (Restaurants and Farms)
Just recently CDC posted that the economic impact of pathogenic food safety outbreaks is $17.6 billion which is $2 billion higher than 2013. The CDC calculates this based on medical expenses, productive decreases in wages, and ultimately loss of American lives. This large number and massive increase in economic cost has made headlines recently as a huge problem, but few in the media understand this number is small compared to the true cost of foodborne illness.
So what is the true cost annually of the collective in the corrective group to the food industry and America as a whole? To come up with that number we need to look at all the costs of an outbreak: Legal costs, fines, bankruptcies, decrease of overall commodity market share, decrease in public trust, and jail time. And let’s not forget, the real cost is that lives were lost due to lack of prevention.
To understand the cost, let’s look at a few examples, starting with Chipotle. Last year the company agreed to pay the largest fine in history of $25 million for its part in multiple outbreaks from 2015–1018 sickening more than 1,000 people. This fine is tiny in comparison to the stock market loss. In 2015 the stock went from $740 a share to a low of $250, and in fact Chipotle’s stock did not get back to $740 until July of 2019. That is billions of market opportunities lost.
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health did a study and concluded that foodborne illness costs the American food service industry $55.5 billion annually. On average each food safety outbreak costs the establishment between $6,330 to $2.1 million, depending on size of the operation and how widespread the outbreak is. Chipotle has a lot of resources to manage and recover from a crisis; many small and/or over-extended companies go bankrupt and are forced to close down.
There are plenty of examples on the supply chain side. The first example is the Salmonella outbreak of Peanut Corporation of America. The largest part of this tragedy is that 714 people got sick, about half of whom were kids, and nine people lost their lives. Due to this, three executives went to jail, not for a few months for decades. The economic cost is astounding; Peanut Corp of America had an annual revenue of around $25 million, but the cost of the outbreak was over $1 billion. This may seem like a very large number, but don’t forget peanuts are an ingredient in many other products. Kellogg’s estimates they lost $65–70 million in products they needed to recall from this one outbreak, and Kellogg’s is just one of many Peanut Corp of America customers.
Another example is the Jensen Farms Listeria outbreak that sickened 147 people and of those 33 died. The brothers, of this multiple generation farm, Eric and Ryan Jenson, went bankrupt and were sentenced to five years probation and six months of home detention; each had to pay a $150,000 fine. Again, this small family’s operations outbreak had massive ramifications for the cantaloupe industry, which suffered significant damage as a result. Walmart reached a settlement for an undisclosed amount in 23 lawsuits involving the Listeria outbreak linked to the cantaloupes
Overall Cost of Prevention: Internal Programs, Supplier Programs, Testing and Audits
The FDA has conducted a few studies on the industry cost of the many leafy greens outbreaks. One study showed the spinach industry alone lost more than $200 million just in retail sales and many more millions in opportunity sales from the 2006 E. coli outbreak. And a recent leafy green outbreak in 2018 cost the industry an estimated $350 million. With staggering numbers like these, the LGMA was created in 2007 to help raise the bar for food safety prevention in this high-risk product. The LGMA study found that their members, which are large leafy green marketers, including Dole, Taylor Farms and Ready Pack, increased their spending three times for true prevention measures.
What does it look like to go from the corrective group to the preventative group? First you have to make the decision of implementation and get buy-in from your entire team. If you are starting from zero, asking your clients and competitors what standards they are utilizing and being audited to, or should be audited to, is a good starting point. This will help in developing a plan of action.
Once you have the checklist, audit human resources. Do you have a Food Safety and/or QA person or team? Are they capable of guiding the executives on this journey? If not, hire a consultant to help you get started.
Once they are on the journey of prevention, people see their entire operation in a different way. They see risks where they never previously saw them—risks with people, equipment, products, building, and the surrounding area. This can get super overwhelming, but if they don’t panic they will be excited about the future. The paradigm will change and they can build, implement and maintain practices to minimize risks one by one, starting with the biggest risks.
In accounting for the physical costs of prevention, the largest will come from the human resources component. Hiring people to build, implement and manage your food safety program will be your largest expense. Another human resources cost is the continued training for the entire staff on food safety expectations. After that cost drops significantly, annual audits and microbiological testing come into play, and the cost will vary on the size of your operation and the risk of your products. For instance the LGMA study showed on average the cost of their members went from $200,000 to about $600,000 annually for prevention, but these are very large multiregional organizations with a very high risk product.
The most important things in life come with hard work and at a price. Every person who has climbed Mount Everest did so one step at a time. Food safety prevention is no different. Is there a cost in money, time, and stress? Yes. Is that cost less than sitting on the beach with your head in the sand of the correction camp? No doubt. But the choice of leaving the majority that are wrong to the minority that are right is yours. Hopefully, you make the right decision.