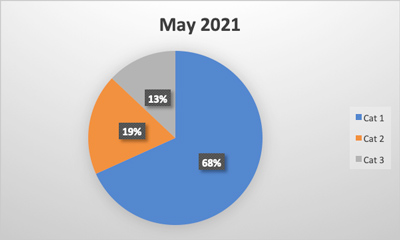
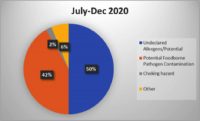
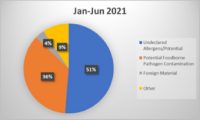
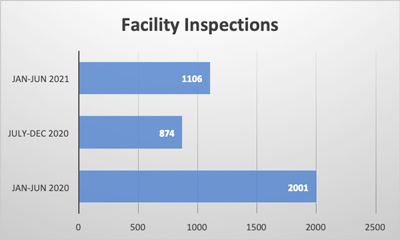
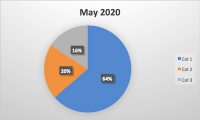
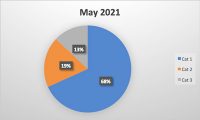
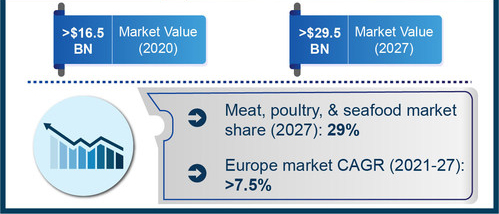
Reading the news in recent months, it seems like there is a new outbreak every week or at least a new recall of various food products contaminated with Listeria, specifically Listeria monocytogenes. Companies have recalled broccoli, kale, cantaloupes, smoked salmon (lox), mushrooms, soft cheese, sprouts, frozen chicken, and even hot dog buns in the last several months.
Listeria monocytogenes is a species of pathogenic bacteria that is very unique. Unlike many pathogens that are mainly fecal bacteria, like E. Coli and Salmonella, Listeria can be found just about anywhere including soil, water, dust and animal feces, to name a few.
We are around Listeria all the time. For example, when moms encourage their children to play outside to enhance their immune systems, one of the bacteria kids are likely exposed to is Listeria. This kind of exposure is generally acceptable, as the vast majority of people that get sick from Listeria exposure typically ingest quite a bit of it. That’s why it is essential to get in front of Listeria to avoid ready-to-eat products from becoming contaminated.
Listeria is one of the few bacteria to survive freezing temperatures and grow, albeit slowly, in a refrigerator. The exact range for growth of Listeria is 39.2°F (4 °C) to 98.6°F (37°C). To successfully kill Listeria using temperature controls, it must be cooked at least at 165°F (73°C). Left at room temperature, the pathogen grows rapidly. If you have ready-to-eat food contaminated with Listeria and it is taken out of the fridge, left on the counter for a couple of hours, then eaten, it’s a recipe for disaster.
If you are healthy, the vast majority of the Listeria bacteria will be attacked and killed by the immune system, preventing the ability for infection to take hold. If the immune system is compromised by conditions such as cancer, AIDS, pregnancy, geriatrics, etc., then Listeria becomes an infection called Listeriosis—an invasive infection.
The FDA and the CDC published some facts about Listeriosis and foodborne illness in general, and the diagnosis is stark. The FDA estimates that 1 in 6 Americans or 43 million people will get a foodborne illness annually. Of those that get sick, the FDA estimates 128,000 will be hospitalized, and about 3,000 die.
In the United States, the CDC estimates that about 1,600 people will get Listeriosis each year, and of those cases, 1,500 will be hospitalized (94%), and 260 will likely die. Listeriosis has a mortality rate of 20-30%, according to the FDA. Unfortunately, these numbers indicate that if the doctor diagnoses you with Listeriosis, the chances of survival are low.
According to FDA research, you are 18 times more likely to contract a Listeriosis infection if you are pregnant, and 16–27% of all Listeriosis infections are in pregnant women. While most other adults show signs of gastrointestinal symptoms once contracting Listeriosis, the FDA says a pregnant woman experiences a fever for a few days, and about 20–30% will ultimately miscarry.
The unique thing about Listeria is the incubation period could last up to 70 days. A possible scenario could be a person eating cantaloupe from a farm with a known Listeria outbreak and then 70 days later showing signs of Listeriosis. This was a reality during the Jensen Farms outbreak, where people were terrified that they may have been infected from Listeriosis after eating cantaloupe. Still, they had to wait for six weeks for assurance they were safe.
What Steps Should Industry Take to Prevent or Mitigate the Presence of Listeria?
The first step is to kill Listeria and prevent it from contaminating food. To kill this particular pathogen, heat and/or sanitization is necessary. The best way to avoid contamination is by cooking food, but cleaning and sanitizing regularly is the next best measure if you can’t cook the product.
All food manufacturing facilities need a cleaning and sanitizing routine. Typically, when a Listeria outbreak occurs, it is because of a series of unfortunate errors in quick succession. Facilities need to practice regularly on finding the potential errors in a cleaning/sanitizing system and fix them immediately. This attention to detail and strategy help correct the problem before an issue arises.
The same is important for the kitchen of a restaurant. Keep raw products away from cooked products. Utilize different sections within the kitchen to prep food in various stages, use separate cutting boards and be sure to use different utensils on raw vs. cooked food. Also, have a solid cleaning and sanitizing routine to kill lingering Listeria in the facility.
The second step is a solid continual testing regimen. A testing rotation is an effective tool in the pathogen prevention arsenal. Every facility should utilize an environmental testing program that regularly looks for Listeria in the facility. While all use outside certified labs, some also have in-house labs looking, more frequently, for pathogens. For instance, few fresh produce companies test the wash water for pathogens in every lot. If they find even the smallest trace of any pathogen, including Listeria, they trash it.
Another effective testing technique is “search and destroy”. In the “Search” process your team swabs everything in the facility looking for Listeria in the facility. When you do find an area with Listeria then you swab everything within a radius starting with one foot, expanding to three feet, then even wider to six feet, etc. until you find every major contamination point. Flag those areas as hot spots for continual checks in your future testing rotation.
The extremely important step three is the cold chain. Cold chain systems help reduce the growth of foodborne pathogens. To minimize the growth of pathogens, including Listeria, it is important to keep products cold at all times possible. This includes harvesting, packaging, storing, distributing, and especially. Also, consumers can play a role in helping reduce contamination by keeping food cold and putting it in the refrigerator or freezer as soon as possible. Every minute a product is left at room temperature can mean massive bacteria growth.
Step four is knowing where your food comes from. In the food industry, we call this supply chain compliance and traceability. A relationship of trust between food producers, suppliers and consumers is vital for the food industry. Raw and finished food products are moving through the supply chain rapidly, so good communication is crucial so that contaminated products are removed quickly to contain an outbreak and save lives.
With these practices in place, we can keep the Listeria outbreaks to a minimum. However, extra care is recommended if you are pregnant, immunocompromised, or over the age of 65. In fact, the FDA has a list of foods to avoid or at least cook very thoroughly. These include deli meat, raw vegetables, and unpasteurized milk products, to name a few.