Botanical ingredients are important to the food and beverage industries as well as the dietary supplements industry. Botanicals are plants or specific plant parts (leaves, roots, bark, berries, etc.) that are used for particular properties. These properties can be therapeutic or related to color, flavor or other attributes. Botanicals include extracts such as Ginkgo biloba, saw palmetto, and elderberry as well as herbs and spices used in cooking, essential oils, pomegranate juice and extracts, and olive oil. There is a substantial overlap between botanical products used in the herb and supplement industries and those used in foods and beverages. Many “conventional” foods and beverages include botanical extracts or other ingredients to advertise a therapeutic effect.
In 2014, FDA issued a final guidance for industry related to labeling of liquid dietary supplements (vs. beverages). FDA noted, in their rationale for the guidance, two trends:
“First, we have seen an increase in the marketing of beverages as dietary supplements, in spite of the fact that the packaging and labeling of many liquid products represent the products as conventional foods. Products that are represented as conventional foods do not meet the statutory definition of a dietary supplement…and must meet the regulatory requirements that apply to conventional foods.
Second, FDA has seen a growth in the marketplace of beverages and other conventional foods that contain novel ingredients, such as added botanical ingredients or their extracts. Some of these ingredients have not previously been used in conventional foods and may be unapproved food additives. In addition, ingredients that have been present in the food supply for many years are now being added to beverages and other conventional foods at levels in excess of their traditional use levels or in new beverages or other conventional foods. This trend raises questions regarding whether these ingredients are unapproved food additives when used at higher levels or under other new conditions of use. Some foods with novel ingredients also bear claims that misbrand the product or otherwise violate the FFDCA.”
The American Botanical Council (ABC) has been publishing information on the safe, responsible and effective use of botanicals since 1988, including the quarterly journal HerbalGram and a book of herb monographs The ABC Clinical Guide to Herbs. In order to help combat the increasing problem of adulteration in the industry, the Botanical Adulterants Prevention Program (BAPP) was launched in 2010 by ABC along with the American Herbal Pharmacopeia and the University of Mississippi National Center for Natural Products Research. The goal of BAPP is to educate members of the herbal and dietary supplement industry about ingredient and product adulteration through the publication of documents such as adulteration bulletins and laboratory guidance documents. The information in these documents helps ensure the identity, authenticity and safety of botanicals along the supply chain.
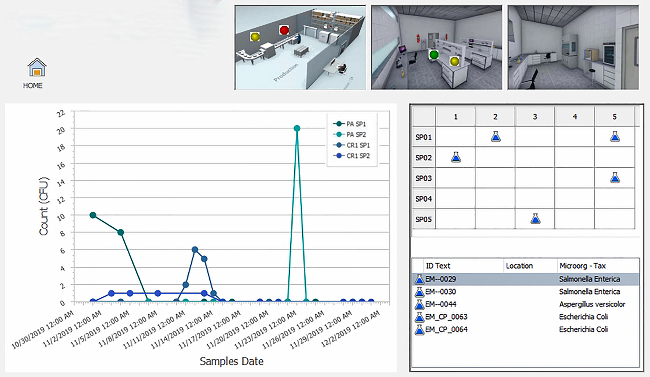
Karen Everstine will be discussing food fraud during the 2020 Food Safety Consortium Virtual Conference Series | An example of the Botanical Adulterants Prevention Bulletin for cranberry is seen in Figure 1. It includes a description of the species that can be labeled as cranberry in the United States, a brief description of the marketplace, information on potential adulterants in cranberry fruit extract and other cranberry products, and guidance on analytical methods to test cranberry products for adulteration.

Decernis has been working with the Botanical Adulterants Prevention Program (BAPP) to integrate links to their expert content into the Food Fraud Database (FFD). This will ensure our users can better develop ingredient specifications, manage risk, and protect their consumers by leveraging this content for food fraud and herbal ingredient fraud prevention. We are currently incorporating three types of BAPP documents into FFD:
- Adulterants Bulletins. Information and links to these documents will be entered as Inference records in FFD. We are extracting ingredient and adulterant names (including Latin names as synonyms) from the document, assigning “Reasons for Adulteration,” and providing a link to the full document on the BAPP website.
- Adulteration Reports. Information and links to these documents will also be entered as Inference records in FFD. We are extracting ingredient and adulterant names from the document, assigning “Reasons for Adulteration,” and providing a link to the full document on the BAPP website.
- Laboratory Guidance documents. Information and links to these documents will be entered as both method record and inference records in FFD. We are extracting ingredient and adulterant names from the document, assigning “Reasons for Adulteration,” and providing a link to the full document on the BAPP website.
Decernis analysts are currently integrating this content into FFD, which will be uploaded to the system between now and early September.