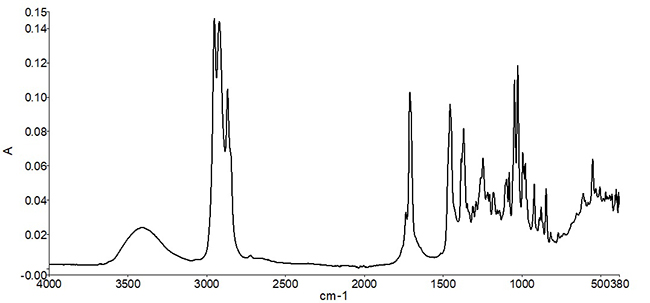
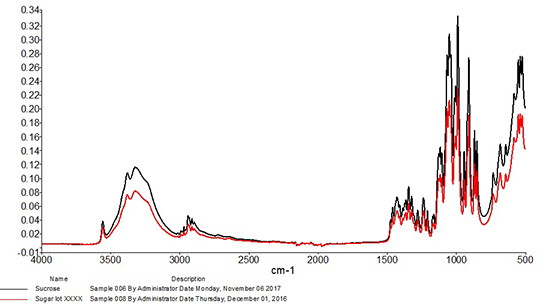
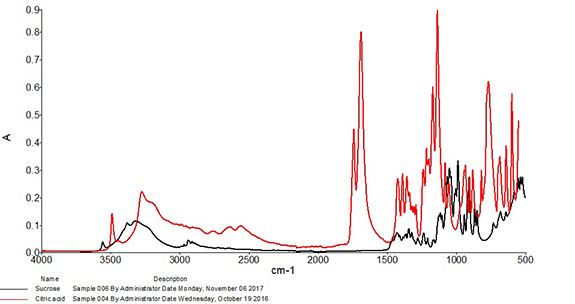
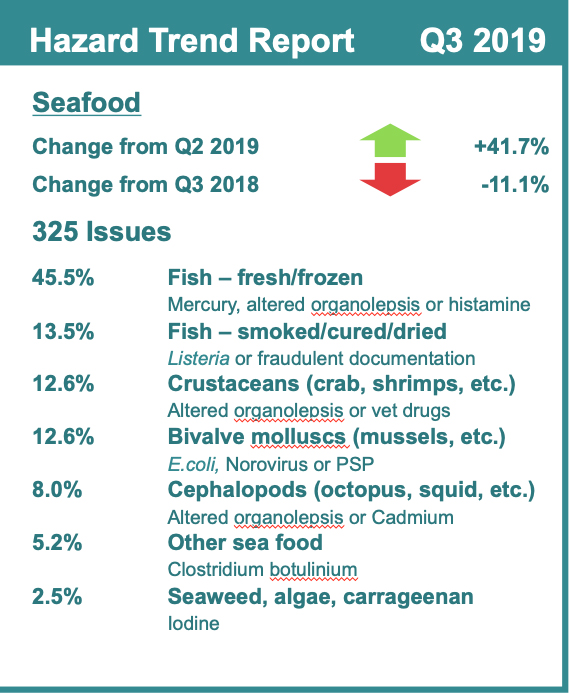
Visibility, accountability and traceability are paramount in the agriculture industry, says Allison Kopf, founder and CEO of Artemis. In a Q&A with Food Safety Tech, Kopf explains how growers can take advantage of cultivation management platforms to better arm them with the tools they need to help prevent food safety issues within their operations and maintain compliance.
Food Safety Tech: What are the key challenges and risks that growers face in managing their operations?
Allison Kopf: One of the easiest challenges for growers to overcome is how they collect and utilize data. I’ve spent my entire career in agriculture, and it’s been painful to watch operations track all of their farm data on clipboards and spreadsheets. By not digitizing processes, growers become bogged down by the process of logging information and sifting through old notebooks for usable insights—if they even choose to do that.

I was visiting a farm the other day and the grower pulled out a big binder. The binder contained all of his standard operating procedures and growing specifications for the varieties he’s grown over the past 20 years. Then he pulled out a pile of black notebooks. If you’ve ever worked on a farm, you’d recognize grower notebooks anywhere. They’re used to log data points such as yield, quality and notes on production. These notebooks sit in filing cabinets with the hopeful promise of becoming useful at some point in the future—to stop production from falling into the same pitfalls or to mirror successful outcomes. However, in reality, the notebooks never see the light of day again. The grower talked about the pain of this process—when he goes on vacation, no one can fill his shoes; when he retires, so does the information in his head; when auditors come in, they’ll have to duplicate work to create proper documentation; and worse, it’s impossible to determine what resources are needed proactively based on anything other than gut. Here’s the bigger issue: All of the solutions are there; they’re just filed away in notebooks sitting in the filing cabinet.
Labor is the number one expense for commercial growing operations. Unless you’re a data analyst and don’t have the full-time responsibilities of managing a complex growing operation, spreadsheets and notebooks won’t give you the details needed to figure out when and where you’re over- or under-staffing. Guessing labor needs day-to-day is horribly inefficient and expensive.
Another challenge is managing food safety and compliance. Food contamination remains a huge issue within the agriculture industry. E. coli, Listeria and other outbreaks (usually linked to leafy greens, berries and other specialty crops) happen regularly. If crops are not tracked, it can take months to follow the contamination up the chain to its source. Once identified, growers might have to destroy entire batches of crops rather than the specific culprit if they don’t have appropriate tracking methods in place. This is a time-consuming and expensive waste.
Existing solutions that growers use like ERPs are great for tracking payroll, billing, inventory, logistics, etc., but the downside is that they’re expensive, difficult to implement, and most importantly aren’t specific to the agriculture industry. The result is that growers can manage some data digitally, but not everything, and certainly not in one place. This is where a cultivation management platform (CMP) comes into play.
FST: How are technologies helping address these issues?
Kopf: More and more solutions are coming online to enable commercial growers to detect, prevent and trace food safety issues, and stay compliant with regulations. The key is making sure growers are not just tracking data but also ensuring the data becomes accessible and functional. A CMP can offer growers what ERPs and other farm management software can’t: Detailed and complete visibility of operations, labor accountability and crop traceability.
A CMP enables better product safety by keeping crop data easily traceable across the supply chain. Rather than having to destroy entire batches in the event of contamination, growers can simply trace it to the source and pinpoint the problem. A CMP greatly decreases the time it takes to log food safety data, which also helps growers’ bottom line.
CMPs also help growers manage regulatory compliance. This is true within the food industry as well as the cannabis industry. Regulations surrounding legal pesticides are changing all the time. It’s difficult keeping up with constantly shifting regulatory environment. In cannabis this is especially true. By keeping crops easily traceable, growers can seamlessly manage standard operating procedures across the operation (GAP, HACCP, SQF, FSMA, etc.) and streamline audits of all their permits, licenses, records and logs, which can be digitized and organized in one place.
FST: Where is the future headed regarding the use of technology that generates actionable data for growers? How is this changing the game in sustainability?
Kopf: Technology such as artificial intelligence and the internet of things are changing just about every industry. This is true of agriculture as well. Some of these changes are already happening: Farmers use autonomous tractors, drones to monitor crops, and AI to optimize water usage.
As the agriculture industry becomes more connected, the more growers will be able to access meaningful and actionable information. Plugging into this data will be the key for growers who want to stay profitable. These technologies will give them up-to-the-second information about the health of their crops, but will also drive their pest, labor, and risk & compliance management strategies, all of which affect food safety.
When growers optimize their operations and production for profitability, naturally they are able to optimize for sustainability as well. More gain from fewer resources. It costs its customers less money, time and hassle to run their farms and it costs the planet less of its resources.
Technology innovation, including CMPs, enable cultivation that will provide food for a growing population despite decreasing resources. Technology that works both with outdoor and greenhouse growing operations will help fight food scarcity by keeping crops growing in areas where they might not be able to grow naturally. It also keeps production efficient, driving productivity as higher yields will be necessary.
Beyond scarcity, traceability capabilities enforce food security which is arguable the largest public health concern across the agricultural supply chain. More than 3,000 people die every year due to foodborne illness. By making a safer, traceable supply chain, new technology that enables growers to leverage their data will protect human life.