During the production process, physical hazards can contaminate food products, making them unfit for human consumption. According to the USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS), the leading cause of food recalls is foreign material contamination. This includes 20 of the top 50, and three of the top five, largest food recalls issued in 2019.
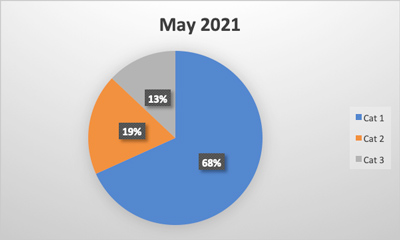
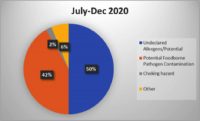
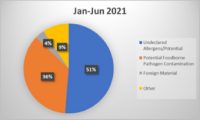
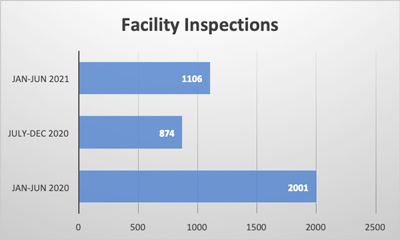
As methods for detecting foreign materials in food have improved over time, you might think that associated recalls should be declining. To the contrary, USDA FSIS and FDA recalls due to foreign material seem to be increasing. During the entire calendar year of 2018, 28 of the 382 food recalls (7.3%) in the USDA’s recall case archive were for foreign material contamination. Through 2019, this figure increased to approximately 50 of the 337 food recalls (14.8%). Each of these recalls may have had a significant negative impact on those brands and their customers, which makes foreign material detection a crucial component of any food safety system.
The FDA notes, “hard or sharp foreign materials found in food may cause traumatic injury, including laceration and perforation of tissues of the mouth, tongue, throat, stomach and intestine, as well as damage to the teeth and gums”. Metal, plastic and glass are by far the most common types of foreign materials. There are many ways foreign materials can be introduced into a product, including raw materials, employee error, maintenance and cleaning procedures, and equipment malfunction or breakage during the manufacturing and packaging processes.
The increasing use of automation and machinery to perform tasks that were once done by hand are likely driving increases in foreign matter contamination. In addition, improved manufacturer capabilities to detect particles in food could be triggering these recalls, as most of the recalls have been voluntary by the manufacturer.
To prevent foreign material recalls, it is key to first prevent foreign materials in food production facilities. A proper food safety/ HACCP plan should be introduced to prevent these contaminants from ending up in the finished food product through prevention, detection and investigation.
Food manufacturers also have a variety of options when it comes to the detection of foreign objects from entering food on production lines. In addition to metal detectors, x-ray systems, optical sorting and camera-based systems, novel methods such as infrared multi-wavelength imaging and nuclear magnetic resonance are in development to resolve the problem of detection of similar foreign materials in a complex background. Such systems are commonly identified as CCPs (Critical Control Points)/preventive controls within our food safety plans.
But what factors should you focus on when deciding between different inspection systems? Product type, flow characteristics, particle size, density and blended components are important factors in foreign material detection. Typically, food manufacturers use metal and/or x-ray inspection for foreign material detection in food production as their CCP/preventive control. While both technologies are commonly used, there are reasons why x-ray inspection is becoming more popular. Foreign objects can vary in size and material, so a detection method like an x-ray that is based on density often provides the best performance.
Regardless of which detection system you choose, keep in mind that FSMA gives FDA the power to scientifically evaluate food safety programs and preventive controls implemented in a food production facility, so validation and verification are crucial elements of any detection system.
It is also important to remember that a key element of any validation system is the equipment validation process. This process ensures that your equipment operates properly and is appropriate for its intended use. This process consists of three steps: Installation qualification, operational qualification and performance qualification.
Installation qualification is the first step of the equipment validation process, designed to ensure that the instrument is properly installed, in a suitable environment free from interference. This process takes into consideration the necessary electrical requirements such as voltage and frequency ratings, as well as other factors related with the environment, such as temperature and humidity. These requirements are generally established by the manufacturer and can be found within the installation manual.
The second step is operational qualification. This ensures that the equipment will operate according to its technical specification. In order to achieve this, the general functions of the equipment must be tested within the specified range limits. Therefore, this step focuses on the overall functionality of the instrument.
The third and last step is the performance qualification, which is focused on providing documented evidence through specific tests that the instrument will performs according to the routine specifications. These requirements could be established by internal and industry standards.
Following these three steps will allow you to provide documented evidence that the equipment will perform adequately within the work environment and for the intended process. After completion of the equipment validation process, monitoring and verification procedures must be established to guarantee the correct operation of the instrument, as well procedures to address deviations and recordkeeping. This will help you effectively control the hazards identified within our operation.
There can be massive consequences if products contaminated with foreign material are purchased and consumed by the public. That’s why the development and implementation of a strong food safety/ HACCP plan, coupled with the selection and validation of your detection equipment, are so important. These steps are each key elements in protecting your customers and your brand.