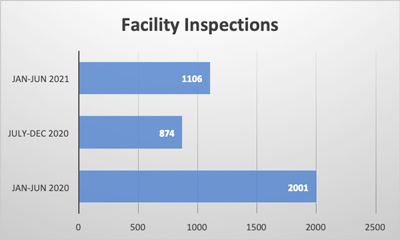
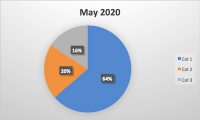
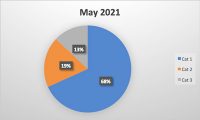
Food safety is an issue that is critical to millions of people’s health every year worldwide. Maintaining a high standard of hygiene is essential in preventing contamination and ensuring all people receive the safest quality food products every time. Inspections and audits are the key components to the industry’s effort to maintain these standards. These processes help identify potential risks and hazards, ensuring companies are compliant with regulatory requirements, and to ultimately protect all people’s health.
Audits and Inspections both verify the facility’s compliance with regulatory and procedural compliance, but in different ways. According to ISO definition, an audit is “systematic, independent, and documented process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which audit criteria are fulfilled.” An inspection is the “determination of conformity to specific requirements,” such as FDA or USDA regulations.
The Importance of Inspections and Audits
Inspections and audits are vital in the food industry for many reasons:
- Preventing Foodborne Illnesses: Regular inspections and audits help the industry identify and mitigate risks that have the potential to lead to foodborne illnesses. This is a very crucial task in preventing outbreaks that can cause severe health issues and even fatalities.
- Regulatory Compliance: The food industry is subject to stringent regulations set by governmental and international bodies. Inspections and audits help to ensure companies are complying with these regulations consistently, avoiding any legal penalties and maintaining consumer trust.
- Quality Assurance: Inspections and audits help ensure food products meet quality standards also, which is very important and essential for companies maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Risk Management: Identifying personal hazards and implementing corrective actions during inspections and audits helps the companies manage and reduce risks associated with food production and distribution.
Inspection Process
Food inspections and audits involve a thorough examination of facilities, processes, and products. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Preparation: Inspectors will review relevant documents, any previous inspection reports, SOPs, and compliance records, to better understand the facility’s history and operations.
- On-site Inspections: Inspectors will visit the facility in order to observe operations, interview staff, and inspect all equipment and outside premises.
- Sampling and Testing: Samples of food products may be collected for laboratory testing to detect contaminants or verify compliance with safety and quality standards.
- Documentation and Reporting: Inspectors will document their findings and provide a detailed report outlining any observations of non-conformances.
- Follow-up: A follow-up inspection may be conducted to ensure all non-conformances have been closed and corrective actions have been implemented and the facility is compliant with all regulations.
Audit Process
Audits are systematic and independent examinations of records, processes, and systems to ensure compliance with specific standards. There are several types of audits in the food industry, including internal audits, supplier audits, and third-party audits. The audit process generally involves the following steps:
- Planning: The audit scope, objectives, and criteria are defined. An audit plan is developed, detailing the audit schedule and then areas to be examined.
- Execution: Auditors will review documents, conduct interviews, and observe operations to gather evidence. They assess compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and company policies.
- Analysis: Auditors analyze the evidence collected to identify areas of non-compliance, potential risks, and opportunities for improvement.
- Reporting: A comprehensive audit report is prepared, highlighting findings, conclusions, and recommendations for corrective actions.
- Follow-up: Auditors may conduct follow-up audits to verify all corrective actions have been implemented and compliance has been achieved.
Food Recalls
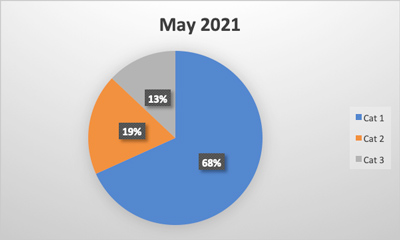
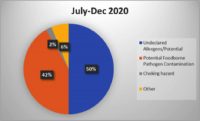
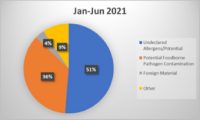
Food recalls are an integral part of the food safety system, initiated when a product is found to be contaminated or mislabeled. They are often the result of inspections and audits that identify serious issues. Here are a few notable statistics.
- There were 547 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) food recalls in 2023, a five-year high for the industry and 19.6% more events than were recorded in 2022. FDA recalls are on track in 2024 to be consistent with 2023. U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) recalls also increased, rising 31% from 2022. The volume of units recalled also increased a more notable 132.8% from 2022 to 2023.
- In 2023, 313 food products (224 from FDA, 89 from USDA) were recalled, over 1,100 people were sickened and 6 people died from foodborne illness recalls (based on data collected). The two largest recalls, lead-tainted applesauce sickened 519 children in 44 states, and Salmonella contaminated cantaloupe sickened over 400 people. CDC estimates 48 million people get sick, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die from foodborne diseases each year in the United States.
- 2% of all FDA recalls stemmed from undeclared allergens, a 27% increase from 2022. One reason for the increase in allergen recalls is as of Jan. 1, 2023, manufacturers had to disclose sesame in their foods. The most common undeclared allergens — wheat, shellfish, eggs, fish, peanuts, milk, tree nuts and soybeans — account for 90% of all food allergic reactions. Listeria was listed as second and Salmonella third for the most recalls.
- Unsurprisingly, as the nation’s largest producer of food, California was found to be responsible for the largest share of all recalls. Over 16.3% of recalls originate from California products. Followed by New York at 8.1% and Texas at 6.5%. California customers are also most frequently affected by recalls. 39.8% of all recalls nationally impact residents in California, followed by New York at 36.4% and Pennsylvania at 35.8%.
The Role of Technology in Inspections and Audits
Advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the effectiveness of inspections and audits in the food industry. Some key innovations include:
- Data Analytics: Big data analytics enable companies to identify trends and potential risks by analyzing large volumes of data from various source, such as inspection reports, consumer complaints, and laboratory results.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology provides a transparent and immutable record of the entire food supply chain, making it easier to trace the origin of products and detect potential issues quickly.
- IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as sensors and RFID tags, provide real-time monitoring of conditions like temperature and humidity, ensuring that products are stored and transported under optimal conditions.
- Mobile Inspection Tools: Mobile applications and digital platforms streamline the inspection process by allowing inspectors to record findings, take photos, and generate reports on-site, reducing paperwork and improving efficiency.
Inspections and audits are indispensable components of the food industry’s efforts to ensure safety, quality, and compliance. They play a crucial role in preventing foodborne illnesses, managing risks, and maintaining consumer trust. As the technology continues to advance with properly trained and calibrated auditors, the effectiveness and efficiency of inspections and audits will only improve, further safeguarding the food supply chain from the farm to the table.
By understanding the crucial role inspections and audits play, stakeholders in the food industry can better prepare to meet the high standards necessary to ensure that food products are safe for consumption. The continued evolution of these processes, bolstered by technological advancements, promises a safer future for consumers worldwide.
Reference:
- Trace One analysis of 2020–2024 FDA and USDA data