Preparation is the key to success for any ongoing endeavor. In an industry where your enemies are fighting for survival at the expense of your business, you must be ready for anything. Your opponents are crafty, adaptable and more prevalent than you think.
No, I’m not describing your competitors. I’m talking about pests—a major threat to the integrity of food products and a threat to any facility’s bottom line. Whether it’s stored product pests contaminating inventory or rodents spreading pathogens as they skitter across equipment, pests are a risk that should be minimized.
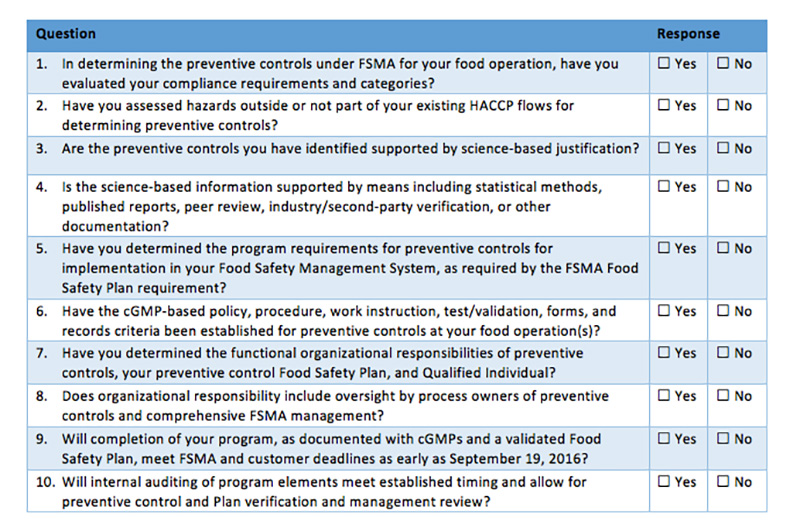
With FSMA in full effect, preparation is more important than ever. FSMA mandates a proactive approach to food safety, and by extension, pest management. It’s important that the pest management program is exhaustive and integrates seamlessly into the overarching food safety plan.
Most, if not all, food processing facilities currently use an integrated pest management (IPM) program to help minimize the chance of pest problems, but FSMA puts more emphasis on being proactive to keep pests far from products at all times. Naturally, this doesn’t mean that a pest sighting in a facility is the end of the world, but it means that it should be resolved quickly, investigated and documented to help prevent such an occurrence from happening again.
Specifically, FSMA has numerous stipulations that trickle down to pest management.
- Hazard analysis. First, a comprehensive inspection should be done to identify the high-risk areas in your facility where pests may take residence. Entry points, potential food and water sources and harborage areas should all be noted.
- Preventive controls. Include regular facility maintenance reviews and a strict sanitation regimen in your food safety plan to help minimize the use of chemical pest management treatments.
- Monitoring. Use devices and employees to keep tabs on pest activity and conducive conditions to ensure preventive controls are working and executed across the facility.
- Corrective actions. Implement and enforce pest management solutions such as exclusion strategies (e.g., weather-stripping, door sweeps, vinyl strip doors), traps (e.g. pheromone traps, insect light traps, bait boxes), air curtains and repellants to help manage pest activity.
- Verification. Schedule regular service visits with your pest management professional to verify corrective actions are working to reduce pest problems over time. These visits should include an annual facility assessment and pest trend analysis, both of which help determine potential areas of improvement over time.
6. Record keeping and documentation. Document every action taken to prevent pests. That includes corrective actions and their results to prove that your written IPM and food safety plan has been implemented and is effective in helping to manage pests at the facility.
With these key components accounted for, it will be easier to be prepared for pests. But, even still, the real-world implementation of these tactics might not be abundantly clear. That being the case, let’s take a look at what food processing facility managers can start doing today to help protect their facilities and demonstrate a proactive approach to food safety.
So, what’s the best way to be more proactive in preventing pests?
Well, that question has a plethora of possible answers, but four of the most important are sanitation, exclusion, staff training and monitoring.
Sanitation
Perhaps the most important of all, sanitation helps to eliminate two key attractants—food and water—that draw pests inside a facility. Any spot where food particles or moisture is collecting, pests will be looking to find.
But sanitation shouldn’t seem daunting. Here are some actions you can start doing today to step up your sanitation program:
- Wipe down equipment regularly to break down the buildup of organic materials.
- Wipe off countertops and sweep floors in common areas where food is present, then sanitize with an organic cleaner afterwards to eliminate any remaining odors.
- Take out the garbage at least daily, and keep dumpsters at least 50 feet away from the building to avoid giving pests a harborage location nearby with an easy path to get indoors. Make sure to cleanse garbage bins and dumpsters regularly, or they’ll become attractive to pests, too!
Exclusion
A big part of preventing pests from getting inside a facility is simply blocking them out using exclusion.
During an inspection, a pest management provider will walk around the interior and exterior of the facility and look for any potential entry points for pests. They should recommend you seal any cracks and crevices they notice, as many pests can fit through extremely tiny gaps. For example, mice can fit through a hole the size of a dime. Gaps should be sealed with a water-resistant sealant to keep pests and moisture out.
In addition, make sure to keep windows and doors closed as much as possible or use screens to block pests. Automatic doors can help in this way, especially when paired with an air curtain to blow flying pests away from entrances. Pests can often come in through the biggest gap of all: The front door!
Staff Training
It’s always better to have a team behind you. Training employees on the basics of an IPM program and what they can do to help will take some of the weight off your shoulders.
Many pest management providers offer free staff training sessions, which can help employees understand what to look for around their work areas and what to do in the case of a pest sighting. Consider creating your own pest sighting protocol to make it clear what employees should do if and when a pest is spotted. They’ll need to record when, where, how many and what kind of pest(s) were seen at the time to give your pest management provider the best chance to create a customized solution to resolve the issue. If you can catch one of the pests in a container for future identification, that’s even better.
Monitoring
While employees can help by keeping an eye out for pests, it’s important to have ongoing monitoring techniques to measure pest activity around the facility.
Monitoring devices are a great way to do this, and your pest management professional can help you place them strategically around the hot spots in your facility. Fly lights, bait stations, pheromone traps and more can capture pests and serve a dual purpose. First, they’ll reduce pest populations around the facility, and, second, they’ll allow you and your pest management provider to see how many pests are present in certain areas.
Over time, this will give you a feel for which pest issues have been resolved and which continue to be a problem. That can determine the corrective actions taken and the long-term food safety plan, which will demonstrate a commitment to constant improvement. That’s a great thing to have on your side, especially when an auditor happens to stop by.
Documentation
I know, I know—this wasn’t one of the four “answers” listed, but it’s still incredibly important! Documentation helps ensure you get credit for being so prepared.
It’s recommended that facility managers keep a few documents on hand to keep things simple. The food safety plan, annual assessments, sighting reports, a list of service changes over time, a list of monitoring devices and proof of your pest management professional’s certification are all important documents to keep updated and ready to go. That way, you can rest easy knowing you’re prepared at a moment’s notice.
It is never too early to start preparing. Pests aren’t going to stop searching for a food source anytime soon, so don’t stop your proactive efforts to keep them at bay. Your financial department will thank you.