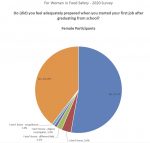
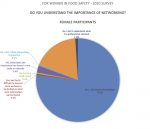
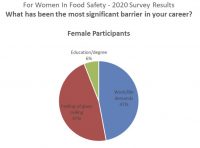
We all know it is important to maintain a healthy work-life balance, regardless of our current career stage. We also know that this can be a challenge. In March 2020 when coronavirus restrictions forced the various aspects of our lives—normally kept separate—to collide in our kitchens and spare rooms, we found ourselves sharing workspace with partners and children. This immediate change really brought our work-life balance into focus.
As part of our Women in Food Safety series, we interviewed three highly successful food safety professionals about how they keep their work-life balance in perspective despite the ever-increasing demands of work, and how they have tackled major life changes or career decisions along the way, while still keeping their career on track.
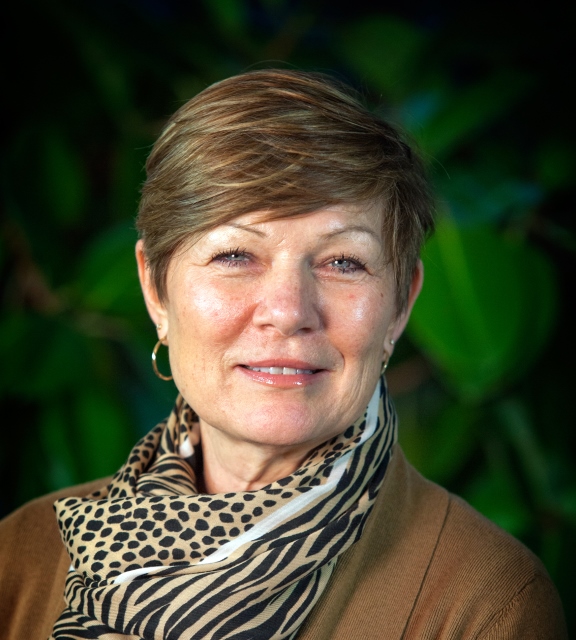
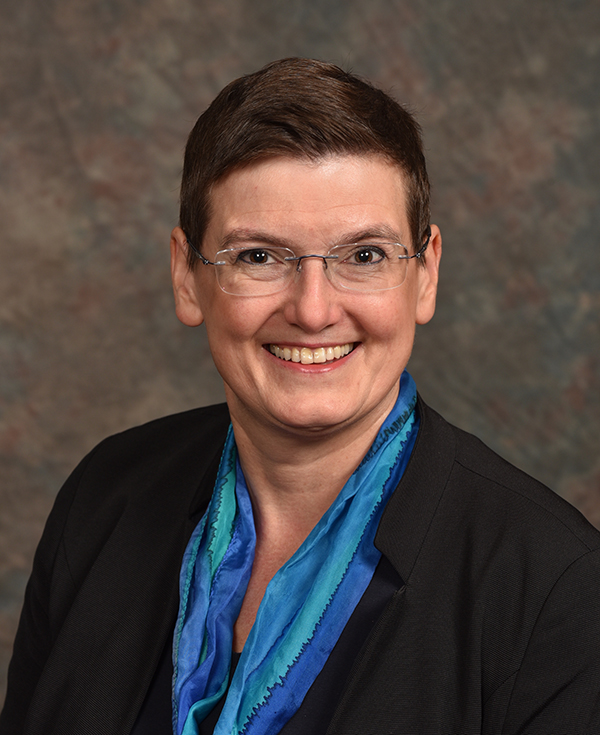
We were delighted to have the opportunity to talk to Shawna Wagner, food sector and technical manager, North America for DNV and SQF Auditor of the Year, 2019; Cornelie Glerum, director of operations for FSSC 22000 and Laura Gutierrez Becerra, food safety regulatory and operations manager at Amazon. These outstanding professional females work in different sectors of the industry and have different career backgrounds, but they all agreed on the importance of keeping a healthy work-life balance and shared surprisingly similar strategies for tackling it. They also agreed that it is all too easy to let work consume your life, so above all, it is very important to like your job and to do something that you enjoy.
It is clear that achieving highly aspiring career goals requires disciplined time management both at work and at home; and it is also important to build a support network of others that can help you. Similarly, although at the start of a career one might think it a sign of weakness to ask for help, this is not true. If there comes a time when it seems impossible to get everything done, be kind to yourself—some tasks can always wait.
Shawna Wagner is a senior auditor so traveling is a major element of her job. Before COVID -19 hit, she might be on the road 270 nights a year. ” This definitely eats into personal time and takes a toll on family life- it is important to switch off at times” she said.
As the director of operations, Cornelie Glerum is a founder, and leading force behind FSSC 22000. She believes that “Work life balance is very important—and that you should work to live—not live to work”.
Laura Gutierrez Becerra has had an interesting and varied career path, which has covered career moves, an international relocation, a family-focused career break as well as the raising of three children before reaching her current position with Amazon. “Work-life balance is important to keep in check. I think that as women, we can forget about ourselves, particularly as we tend to be fully dedicated to our job or career path, or we have family responsibilities or dependents to care and provide for. We tend to put considerations for ourselves last.
There are elements and approaches to maintaining a work-life balance that all of them agreed upon.
1. Keep a personal schedule as well as a work schedule
It is easy to let work overwhelm or occupy your all your time, so it is important to make personal appointments with yourself or your family.

Wagner: I certainly try to schedule something every weekend, such as golf, camping, and dinner events. The scheduling is important as if it’s not in my phone calendar, it’s not happening.
Glerum: I have a family, a partner and two young children, and we do have some family commitments that are on a set schedule such as the Friday hockey practice, which is an important part of my week, as I enjoy being the coach. If they are written into the schedule, it is easy to keep the commitment.
Gutierrez: I am fairly good with this now compared to when I started my career. We had to create schedules for everyone in the family to have responsibilities in the home so that the chores got done, but we also factored in extra-curricular activities such as family game night, etc. We also enjoy exercising together, which is important for us all.
2. Taking time off
Wagner: I have come to learn that vacation time is your time to shut work off, and I was extremely poor at this practice. I would take vacation but still work all day on emails, so I didn’t fall behind for when I was back from vacation. My best advice is to know that it will still be there when you get back and to train others to cover for you for when you are not in the office. Also return the favor for others, as we all deserve downtime.

Gutierrez: There was a point in my career when I was juggling job moves raising children with different ages (an infant, a toddler and a teenager) , and I felt burnt out. I took the great piece of advice from my mentors who advised me to do more of the hobbies that I enjoy, and to learn to delegate. Although this was difficult at first, it was helpful to consider delegation as a way of helping others to develop and advance their careers. Looking at it from this [perspective] allowed me to take some time off.
3. Keep your phone in check. While of course it is a life-changing invention, the cell phone is also the never-ending connection to work.
Wagner: I keep things in perspective by always having dedicated time to my family and friends. For example, if I am having dinner with my partner, it’s a hard rule that I will not answer the phone.
Glerum: I am aware that I have big responsibilities in my job, so I do tend to stay in touch and keep my phone on even during holidays and vacations, but I try to keep calls at the minimum.
4. Asking for help
Wagner: It is important to ask for help, and if you can find others who want to learn, then it helps them also. When I was new to the industry, I wouldn’t ask for help, as I wanted to show that I could achieve success by myself or seek the right answer for the solution, and I realized that this might not be the good way. We all need to learn to be comfortable to ask for help.

Glerum: Yes, I can ask for help, and I am fortunate to have my parents close by so I can ask to help with children if I am at work or traveling. I also have good neighbors that can step in, and this works both ways. This is truly a valuable support network, and we all help each other with reciprocal arrangements.
Gutierrez: I was not good at the delegating tasks at the beginning. As I had relocated from Mexico to the United States, I did not have any close family here to call on. Also, as is typical of my Mexican culture, I felt I had to do everything myself for my family at home as well as demonstrating at work that I was on top of my game. This was completely wrong and quite self-defeating. Today, I am better at prioritizing and delegating. Developing new networks has also helped me both on a personal as well as professional level. When I moved from Mexico, I didn’t even know how and where to start. However, I have worked specifically to build supportive circles such my “kindergarten mothers”, my “Mexican coffee chat” and of course, my great “Women In Food Safety” network”.
Other Advice We Want Share
Glerum: It is important to recognize that not all jobs need to be done all of the time, and if you are heavily committed at work, some chores just might not get done. While you might be a high achiever, you do not need to set the bar so high for everything. Maybe you do not get all the cleaning done on time in the house, give yourself a break. If the laundry is becoming an issue, and the children are running out of clean clothes—add to the wardrobe, buy more socks for the children!
Gutierrez: Going through life-changing events and overcoming challenging moments for sure gives you resiliency and provides realization that we women can overcame many things. I have had several major changes in my home life. However, I can fully relate to the expression: “A women is like a tea-bag, you don’t know how strong she is until you put her in hot water” by Eleanor Roosevelt.
Preparing to Start Your Career? Here’s Some Advice
Wagner: Women can do any job and can be developed to achieve their goals. Women also provide an important perspective to the mixture of different people with whom you work. The field of food safety also is open to many career aspirations. I recently did an audit at a facility where a young lady was the maintenance manager. She rocked that shop!
Glerum: As women, we have a range of different skills and strengths in the workplace. We are good with precise details, are conscientious and demonstrate accuracy, which is important in my business as a certification program owner. We should use these different attributes to our own advantage in the workplace without compromise. However, women often do not always have enough confidence in their abilities and are sometimes afraid to speak up, especially in a man’s world.
Women also add an “elegance” for want of a better world, which can add to the comfort and refinement to the workplace. For example, we are more likely to remember birthdays and see the importance of staff appreciation, sharing gifts etc. This makes a nicer workspace for everyone.
Gutierrez: Do not to be afraid of asking questions. I initially lacked confidence to ask questions. Also, ask for feedback. It is very important and always helpful, whether it is positive or negative, learn from it and actively apply this learning. Always be open to new opportunities, be inquisitive about other areas. If you do not see opportunities for learning and development, move on to somewhere else if you can. Constantly, assess your aspirations and determine what is your main drive.
Do what you like and like what you do!
Women are an important element in the workplace and the home. Balancing work, life and the demands of a family can take a heavy toll. However, supporting networks can help. Feel free to reach out to Women in Food Safety so we might offer some support and advice—you are never alone.