Alan Baumfalk is Pet Food Safety Specialist and food safety Auditor at Eurofins US Foods Division. After more than three decades of experience in human food production facilities, Baumfalk began inspecting and auditing pet food companies with a fresh pair of eyes and in his opinion, “pet food plants typically are very well maintained, embrace technology, are highly automated, have great productivity and are very efficient with their sanitation and production.”
In an interview with Food Safety Tech, Baumfalk talks about differences in production of human food and pet food; lessons learned from historical incidents such as melamine in pet food and contaminated chicken jerky; what are some gaps in pet food safety he’s noticing and impact of the Food Safety Modernization Act or FSMA on this sector.
Food Safety Tech (FST): What are the differences between the production of human food and pet food?
Baumfalk: In most cases, pet food facilities are dry facilities, making kibbles and similar products, and their cleaning sanitation processes are mostly sweeping and dusting, with very little water involved. When it comes to regulations covering pet food facilities, most of these fall under FDA jurisdiction, and pet food facilities need to have in place risk-based HACCP plans to ensure food safety. Some of the challenges involved in pet foods are how do you do sensory testing on dry pet food or test for taste or consistency? Pet food testers look at certain quality attributes such as color, look, smell and taste of the product. They look for data such as amount of protein in the food etc. They also need to consider if humans – especially the elderly, or children – would consume the pet food product, because this can have many food safety implications.
FST: Humans have allergic reactions to certain food ingredients. Do pets have similar concerns of allergens?
Baumfalk: We don’t know if pets suffer allergic reactions to any specific food ingredients similar to humans. Pet food manufacturers are not subject to allergens and are exempt under FDA’s allergen management regulations. However, there are strict GMPs maintained in pet food production facilities, so that known allergens are identified. Pet food manufacturers give attention to allergens though they are exempt because it’s possible that the allergens could get transferred to a human in the house who could be allergic to nuts or soy, and this could be a huge problem. In our experience, we have seen that pet food can be occasionally consumed by a child or an elderly pet owner, out of curiosity.
FST: How about pathogens such as Salmonella and E.coli, are pets susceptible to these?
Baumfalk: Pets are not typically affected by pathogens such as Salmonella or E.coli, and this goes back to their genetic background, which is, dogs coming from wolves, and cats from tigers and lions. These animals are used to eating things with pathogens, fecal matter etc. However, humans are at risk of infection by Salmonella and E.coli, so while the end consumer of pet foods are not affected by these pathogens, their handlers are. Hence, pet foods are tested for Salmonella and E.coli to make sure they are pathogen free. They have Critical Control Points (CCPs) and kill-steps just like human foods, and pet foods are diligently sampled before they are released in the market. Environmental monitoring is also strictly carried out – such as extensive swabbing of processing floor, walls etc. to test for Salmonella/ E.coli/ mycotoxins etc. If a raw material exceeds FDA guidance for mycotoxins, then they are rejected. Many manufacturers test for mycotoxin levels in finished product as well.
FST: Are there differences in auditing pet food companies versus human food manufacturers?
Baumfalk: All pet food companies are looking to get certified and audited under a GFSI-recognized scheme. SQF is probably the biggest standard though some choose BRC. Eurofins has close ties with the American Feed industry Association (AFIA) which recommends SQF, and so we follow the same standard when auditing pet food facilities. SQF has modules specific to pet food category and dry pet food products. There are a lot of similarities with requirements for human food – for instance, pest control within a pet food plant is the same as within a human plant. The commitment and requirement for compliance is the same.
FST: What are some gaps or challenges in pet food safety?
Baumfalk: Most of the folks working in the pet food industry have a background in human food and are very much aware of the technical and regulatory requirements for making human food, so they end up carrying it over to pet food production. They typically follow GMPs and HACCP, and safety plans to ensure there are no food safety gaps. While most pet food companies meet, or even exceed, compliance requirements, there are always some people in the industry that don’t get the message.
FST: When we think about pet food safety, the history of melamine contamination of pet food, and tainted chicken jerky from China come to mind. What are lessons learned and how can the pet food industry be prepared for the unknown?
Baumfalk: The melamine adulteration and chicken jerky contamination incidents have taught the industry to be on guard. The industry has to make sure that they are in close alignment with their industry association which speaks for them, read technical documents, hire and train knowledgeable staff – all of which helps constantly look for the next thing that we weren’t aware of. Apart from diligently monitoring the global supply chain, it would help to have strict audit specifications for global suppliers. If something is coming from the other part of the world, where there’s a history of food safety standards not always being up to par, the pet food industry needs to make sure to buy only from a known and approved entity. Also look for lessons that can be learned from the human foods industry. Read about recalls and withdrawals and find out why that happened, if the pet food industry has similar exposure, and how this can be addressed.
FST: What will be the impact of the proposed pet food safety rule under FSMA be on this industry?
Baumfalk: FSMA is going to tighten things up, paying a lot of attention to the global supply chain and any vulnerabilities. While regulations are still being finalized, the pet food industry is already aligning itself with these proposed regulations. The technical and regulatory folks in the industry are following it; they are reading food safety journals and interacting with their associations for guidance and for making comments on the regulations. We are also updating our auditing checklists to see how we can align better with new FSMA requirements.
For more information on Eurofins, it’s pet food and auditing capabilities, click here.


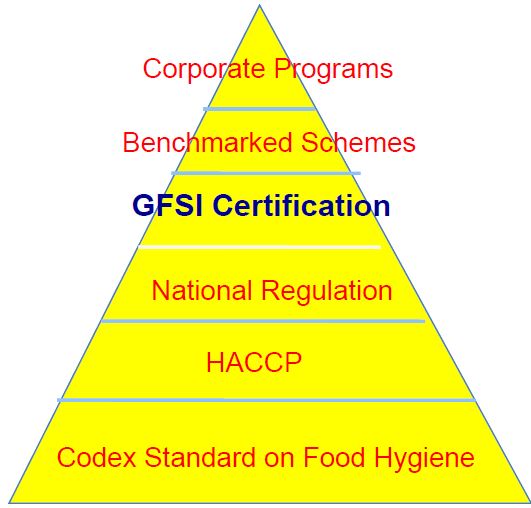

 At the very base of our efforts that are ensconced within these guidance on a sector by sector basis, are the international standards of science based within the Codex Standard on Food Hygiene. On top of that are Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points or HACCP standards. Above HACCP are National Regulations, which includes FSMA in the U.S. and the Safe Food for Canadians Act in Canada. In Europe it’s something different, in Japan it’s something different, but all have iterative levels of science-based regulation in place to ensure the safest control of the food and management of the food. Above National Regulation is GFSI Certification.
At the very base of our efforts that are ensconced within these guidance on a sector by sector basis, are the international standards of science based within the Codex Standard on Food Hygiene. On top of that are Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points or HACCP standards. Above HACCP are National Regulations, which includes FSMA in the U.S. and the Safe Food for Canadians Act in Canada. In Europe it’s something different, in Japan it’s something different, but all have iterative levels of science-based regulation in place to ensure the safest control of the food and management of the food. Above National Regulation is GFSI Certification.



