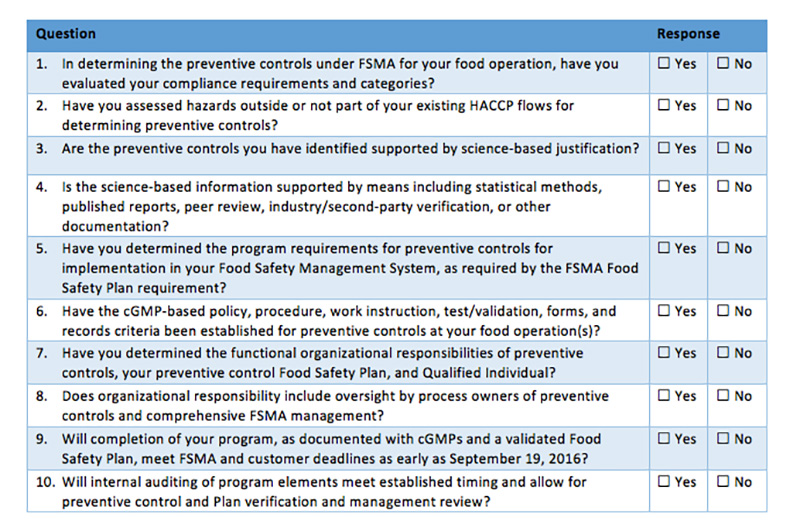
Confusion reigns in many organizations and especially with our food safety and quality professionals, as we debate and attempt to decide how best to address the requirements of FSMA. With the first compliance date of September 2016 drawing near, companies are feeling increased pressure to take action. As many are already accredited to a GFSI-approved food safety scheme such as SQF Level 3, BRC, Primas, IFS or FSSC 22000, often the question is, how does my current system fit into FSMA, and where do I need to make changes? The undercurrent to this question is the implication that changing the system to fit FSMA will cause it to no longer be tailored for the desired GFSI food safety scheme, and that a change could cause issues with those audits (which are crucial for purchasing, marketing and sales).
The Food Safety Consortium will discuss critical industry issues, including FSMA compliance. The event takes place in Schaumburg, IL | December 5–9, 2016 | LEARN MOREAs with so many of our industry challenges, there is no easy and prescriptive answer to these questions. Each organization has to make the decision for their own system based on their individual hazard analysis, risk tolerance and resources. Some over-arching themes begin to emerge, which may be analyzed to assist the decision makers in the creation of a road map to FSMA compliance.
During our FSMA Preventive Control Qualified Individual (PCQI) training courses we are repeatedly asked, “What qualifies as a preventive control? Are our critical control points (CCPs) automatically a preventive control? How about our operational prerequisite programs (OPRPs)—are these PCs also?” While there is no easy answer (yes or no), there are some important things to keep in mind that can help in the decision.
The official answer is that a preventive control should be any point in the process where, with a loss of control, it is reasonably foreseeable that a significant food safety hazard either will occur or has an increased likelihood of occurrence. Remember this is intended to be a single point in the process, not the entire process. For example, the sanitation program may be managed as a prerequisite program; however, there may be a point in the process that requires special sanitation attention and without it, there is a reasonably foreseeable likelihood of a hazard.
Thinking about the concept, a logical conclusion is that a loss of control leads to a significant food safety hazard or, at the very least, increases the likelihood of said hazard. It follows that a loss of control would beget the need for a withdrawal if the product had already left the organization’s control. Therefore, one should only designate a point as a preventive control if the implications of conducting a recall in the event of failure have been analyzed as part of the risk assessment. The organization must be fully prepared to conduct such a recall in the event of failure.
The FSMA Preventive Control regulation (§21CFR117.135 – Preventive Controls) requires a recall program only if there is a preventive control identified in the process. Of course, any food processing organization would be remiss if they did not have an effective recall program defined and tested by regular mock recalls. Waiting for a true recall is no time to find out that your program has issues. Even without a preventive control, what happens if a supplier contacts the processor with an issue that requires a recall?
Through the evolution of compliant and mature food safety management systems, it is common for an organization to initially identify multiple CCPs and then, through data collection and process improvements, slowly reduce the CCPs to control points managed through OPRPs or PRPs over time. So, should an OPRP (Operational Prerequisite Program – ISO 22000:2005 Section 7.5) also be designated preventive control? This is perhaps one of the grayest of gray areas in this arena. A deviation in a preventive control, if the product has left the organization’s control, requires a recall. A recall for a deviation in an OPRP is not absolute, and it is actually handled by the food safety team and management on a case-by-case basis, depending on the risk. In addition, although identified when possible, a critical limit is not required for an OPRP (ISO 22000:2015 Section 7.5). Parameters are required for a preventive control.
There really isn’t one answer that fits every situation, but it is important to remember that the requirements for FSMA Preventive Controls regulation (§21CFR117.135) are designed for those operations that in the past have not had the opportunity to define, implement and maintain a food safety program—one that includes a hazard analysis based on HACCP guidelines (Codex Alimentarius Commission [Annex to CAC/RCP 1-1969, Rev. 3 (2003)]) and/or a GFSI-approved food safety scheme. Personally, we feel that if an organization has evaluated their process in compliance with a GFSI-approved food safety scheme, then any reasonably foreseeable hazards have been identified and addressed through a control point such as a CCP, OPRP or PRP. However, that said, upwards of 90% of recalls are linked to either ineffective or nonexistent PRPs such as allergen mislabeling, which accounted for 53% of all recalls last year. Thus, it is imperative that we evaluate all aspects of our processes with the same scrutiny that we do our microbial pathogen and metal control programs, which are common CCPs in today’s world of food safety.
Risks must be evaluated through an effective risk assessment based on science and facts. We start almost all of our workshops with the great American Society for Quality (ASQ) video: Cost of Poor Quality. This highlights the lack of an effective risk assessment performed on January 28, 1986, related to the launch of the Challenger. Unfortunately, emphasis was not on the fact that the engineers presented about the lack of cold temperature stability of critical O-rings, but rather on the fact that the launch had already been postponed for two days, and there was intense media and political hype surrounding the event. An effective risk assessment must be based on facts and objectivity, not on our feelings about what we want or need the decision to be.
FSMA PCQI training stresses the use of reliable and credible resources such as academia, trade organizations and process authorities. The internet itself can also be a valuable resource. Jon Porter stated in 2004, “HACCP, as we know it, would not exist without the internet.” (If Jon could only see us now.) However, again, we must be sure we are choosing credible information from the internet. We all know that we can usually find any answer we desire on the internet, but is it credible and accurate?
Competent industry sector-experienced consultants may also be good options if the organization ensures their credibility. Sometimes, a set of independent eyes can be just what the doctor ordered. Even in cases where the organization has a fully qualified team that is perfectly capable of managing the food safety program on their own, the right external resource (i.e., consultant) may provide an additional, independent viewpoint to your process. A friendly debate with an external resource can oftentimes open a whole new vista of previously unconsidered possibilities for the team.
The FSMA Preventive Controls regulation (§21CFR117.135) states that “each organization is required to have a PCQI that has successfully completed training in the development and application of risk-based preventive controls at least equivalent to that received under a standardized curriculum recognized as adequate by FDA or be otherwise qualified through job experience to develop and apply a food safety system”. What qualifies an individual to be qualified through job experience is not specifically defined but is judged by the effectiveness of their food safety program. However, if FDA visits the facility and asks for the PCQI and no one has taken an FDA-recognized course—but there is someone that the organization has identified as qualified—this has the potential to start the visit off with a negative focus. We urge each organization to send two food safety associates to an FDA-recognized FSMA PCQI training course regardless of their background (this provides a back-up person in case the primary representative is ill, traveling for business or pleasure, wins the lottery, or otherwise leaves the company, etc.). This provides a strong foundation for the future, as ownership of the system is always crucial to not just surviving an inspection, but excelling—and as food safety professionals that is an idea we can all support.