The food safety testing industry is constantly experiencing new developments, technological advances and regulatory pressures as the burden of foodborne illness remains a prevalent concern. Growing consumer preference for convenience and processed foods is a pivotal trend augmenting the industry outlook.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that every year nearly $110 billion is lost across middle- and low-income countries due to unsafe food. From the health risk perspective, pathogens, pesticides or toxins cause more than 200 diseases, ranging from diarrhea to cancers. Since most foodborne illnesses are preventable, WHO and other public health organizations worldwide are taking necessary action to establish strong and resilient food safety systems and enhance consumer awareness.
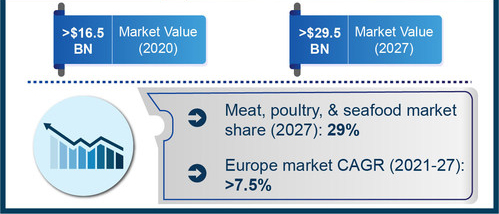
Food products may become contaminated at any stage of production, supply or distribution. Testing food and beverage products for safety is a critical component of the food and beverages sector. In terms of annual valuation, the global food safety testing market size is anticipated to hit $29.5 billion by 2027.
Pathogen Testing Demand Rises as E. coli, Salmonella Infections Persist
Pathogen testing is of utmost importance to the food & beverage industry, as there remains a large number of virus and bacteria causing pathogens and microbial agents responsible for foodborne illnesses. Numerous instances of pathogen contamination have come to light recently, augmenting the need for food pathogen testing, especially during a time when COVID-19 poses a significant threat.
For instance, in July, the CDC and the FDA announced that they are working with other public health agencies to investigate an outbreak of E. coli O121 infections across 11 states. Meanwhile in the European Union, several countries have started investigating Salmonella illnesses linked to imported tahini and halva. Since 2019, about 80 people are estimated to be affected in Germany, Denmark, Norway, Sweden and the Netherlands.
Pathogen testing demand will likely increase across North America and Europe with further spread of infections. These regions are among the major consumers of processed meat, seafood and poultry products, augmenting the need for reliable food safety testing solutions.
Meat, Poultry and Seafood Consumption Drive Foodborne Infection Risks
Globally more individuals are consuming processed poultry and meat products at home, in restaurants, fast food restaurants, and other locations. The worldwide meat consumption is estimated to reach 460 to 570 million tons by the year 2050, as per data from The World Counts.
It is essential to ensure optimum product quality during meat processing to minimize the perils of foodborne microorganisms. Meat quality testing standards are continuously evolving to ensure that food manufacturers bring the best-quality products to the market. In July this year Tyson Foods recalled more than 8.9 million pounds of ready-to-eat chicken products due to potential Listeria monocytogenes contamination. The significant recall quantity itself represents the scope of pathogen testing requirements in processed meat sector.
E. coli O157 is considered to increase the risk of toxins that lead to intestinal problems and can cause significant illness among geriatric people, pregnant women and other high-risk populations. Earlier this year, PerkinElmer introduced an E. coli O157 pathogen detection assay to be used for testing raw ground beef and beef trim. The solution is greatly suited for food and beverage sector customers that need to test high volumes of food samples regularly. The development indicates an incessant fight to offer effective food safety testing products to tackle the threat of pathogen-related illnesses.
USDA’s FSIS also recently revised guidelines for controlling Salmonella and Campylobacter infections in raw poultry. The updated guidelines provide poultry establishments with best practices that they may follow to reduce the risk of such infections in raw products.
Food Safety Testing Trends amid COVID-19 Pandemic
Food safety testing demand has experienced a notable uptick since the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, as food security and sustainability have been recognized as key areas of focus.
Globally, a rise in online orders of groceries and restaurant meals has been observed. Major food regulators such as the FDA have released food safety protocols and guidelines for food companies, hotels and restaurants. These practices help ensure optimum food quality as well as the safety of employees, staff and consumers.
The FDA has been working with the USDA and FSIS as well as state authorities to investigate foodborne illnesses and outbreaks amid the pandemic. Many regions are also updating food safety policies to help overcome the challenges of the pandemic. While pathogen and toxin testing demand are growing in most regions, the inadequacy of food control infrastructure may limit food safety testing industry expansion in emerging economies.
Drawbacks of existing technologies and the need to reduce sample utilization, lead time and testing cost are driving new innovations in food safety testing. Ongoing developments are focused on providing accurate results in limited timespan.
The food safety testing market landscape will continue to evolve as new regulations are introduced, public awareness rises, and food consumption patterns change. The rapid testing technology segment, which includes PCR, immunoassay and convenience testing, is estimated to hold a major share of the overall industry owing to faster results provided, which benefits the organizations in terms of productivity and processing costs. In addition to previously discussed PerkinElmer, Eurofins Central Analytical Laboratories Inc, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Intertek Group PLC, Bureau Veritas SA, and SGS AG are some of the other notable names in the industry.