Many food retailers are dependent on outdated methods of recording product food temperature that include pen, paper and trust given to employees to remember to complete inspections. Unfortunately, this style of inspection completion can be an outlet for foodborne Illness outbreaks. As technologies advance to offer real-time reporting, managing such vital inspections and reports has never been so simple while drastically reducing risk and increasing consumer safety.
Food service management should be asking the following questions on a daily basis:
- What food items passed & failed the cooling/cooking process?
- Why did these items fail and what is the monetary value of product loss?
- Have safety & operational checklist logs been completed on time?
- What corrective actions were issued?
- Have temperature-controlled cases failed within the last 24 hours?
With recent breakthroughs in food safety technology, the answers to the above questions can be found in your email inbox, online dashboard or mobile application. There are technologies available that give food service providers the ability to efficiently track and manage their food safety efforts by digitizing any type of food safety, quality assurance and sanitation inspections. One such technology uses a dual infrared/probe Bluetooth thermometer and real-time temperature sensors to help complete food safety temperature checks as well as bringing automation to cooling, cooking, and “time as temp” logs. This kind of technology can be integrated into food safety and risk management tools such as sensor monitoring or location-driven inspection technology.
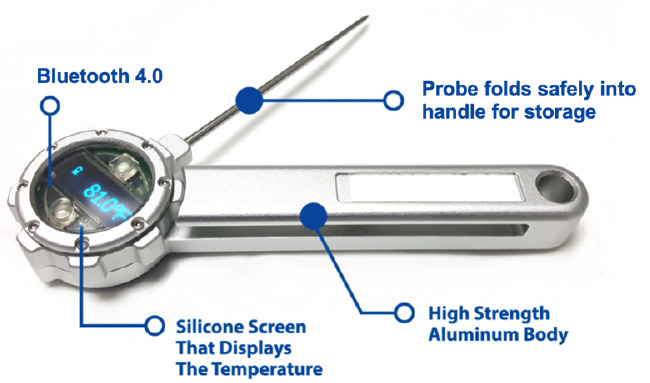
Sufficient inspection software is not just a format for checklist completion. Software developed for the food service industry is behavioral based, meaning the software will guide inspectors to their next question and corrective action; or it automates the processes all together. This includes reminding inspectors when inspections are due in addition to providing snap shots to management on the status of said inspections with the ability to easily pull all data from the cloud.
Automated Logs for Cooking, Cooling and ‘Time as Temp’
Before taking a closer look at how new technology is shaping cooling logs, cooking logs, and time as a public health control; the following are a few terms to remember:
- Cooling & Cooking Logs: Recording of food product temperatures during cooking & cooling cycles that meet both time and temperature constraints outlined by the FDA.
- Time as a Public Health Control: Food product whose holding compliance is measured not by temperature but by time spent in the range of 41° F – 135° F after either being cooled below 41° F or heated above 135° F, as outlined by the FDA.
- Strategy: What is being done with the food product? Is it being cooked, cooled or held for Time as a Public Health Control?
- Phase: Time and/or temperature constraints set within the strategy. For example, cooling product from 135° F to 70° F within two hours or cooking to 165° F before being served.
As one of the most groundbreaking forms of food safety inspections, automated cooling and cooking logs create the ability to customize strategies for such processes. Cooling and cooking logs are an important aspect of food safety for their ability to complete the product lifecycle that can often times be overlooked. Such logs also help to ensure food product is cooked to proper temperatures before it is served to customers. Cooling log strategies look for product to be cooled from 135° F to 70° F within two hours and from 70° F to 41° F within four hours. Cooking logs are built in similar fashion but may vary on the type of product.
Proactive technology allows food service personnel to automate the cooling and cooking process with sensors that record and save product temperatures during cooking and cooling strategies. Once temperature thresholds are succeeded or anticipated to be missed, customized alerts can notify employees that the food is either ready to be served or that action is needed to avoid product loss.
For example, cooling a batch of rotisserie chickens would typically require an employee to manually check the product temperature every 30 minutes to ensure the rotisserie chickens are being cooled properly. With new technology, this same employee can insert a food-grade sensor probe into one or more of the chickens and walk away. The employee can reference a mobile application and real-time push notifications to ensure the chickens are cooling from 135° F to 70° F within two hours and from 70° F to 41° F within four hours. If the software’s algorithms predict that the rotisserie chickens will not meet the conditions set in the phase, proactive push notifications will be sent to the employee for specific action to ensure proper cooling, which avoids product loss and consumer claims related to foodborne illness. Using this method also allows for overnight cooling logs in addition to saving labor hours, all while eliminating paper.
As demand for increased food safety practices continues to climb, so will the capabilities of behavioral based inspection technology. Equipped with industry leading software engineers along with dual purpose customer support and onboarding services, this space will expand on its software and hardware capabilities to replace all outdated methods of inspection processes.








