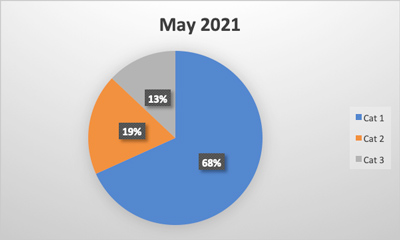
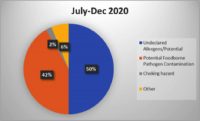
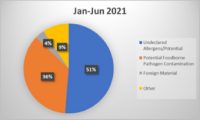
The food allergen testing industry has garnered considerable traction across North America, especially due to the high volume of processed food and beverages consumed daily. Allergens are becoming a significant cause for concern in the present food processing industry worldwide. Food allergies, which refer to abnormal reactions or hypersensitivity produced by the body’s immune system, are considered a major food safety challenge in recent years and are placing an immense burden on both personal and public health.
In 2019, the most common reason behind recalls issued by the USDA FSIS and the FDA was undeclared allergens. In light of this growing pressure, food producers are taking various steps to ensure complete transparency regarding the presence of allergenic ingredients, as well as to mitigate risk from, or possibly even prevent contact with, unintended allergens. One of these steps is food allergen testing.
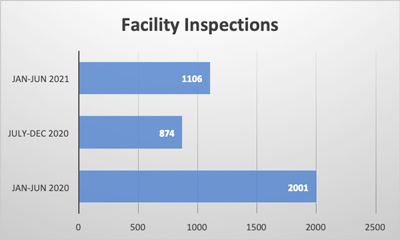
Allergen detection tests are a key aspect of allergen management systems in food processing plants and are executed at nearly every step of the process. These tests can be carried out on work surfaces, as well as the products, to detect any cross contamination or allergen presence, and to test the effectiveness of a food processing unit’s cleaning measures.
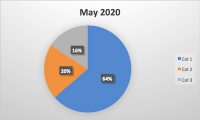
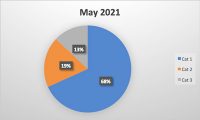
There has been a surge in awareness among consumers about food allergies and tackling the risk of illnesses that may arise from consuming any ingredient. One of the key reasons for a higher awareness is efforts to educate the public. In Canada, for example, May has been designated “Food Allergy Awareness Month”. It is estimated that more than 3 million people in Canada are affected by food allergies.
The size of the global food allergen testing market is anticipated to gain significant momentum over the coming years, with consistent expansion of the dairy, processed food and confectionary segments.
Understanding the Prevailing Trends in Food Allergen Testing Industry
Food allergies risen nearly 50% in the last 10 years, with a staggering 700% increase observed in hospitalizations due to anaphylaxis. Studies also suggest that food allergies are a growing health concern, with more than 250 million people worldwide estimated to be affected.
Although more than 170 foods have been identified as causing food allergies in sensitive consumers, the USDA and the FDA have identified eight major allergenic foods, based on the 2004 FALCPA (the Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act). These include eggs, milk, shellfish, fish, peanuts, tree nuts, soybean, and wheat, which are responsible for 90% of allergic reactions caused due to food consumption. In April 2021, the FASTER (Food Allergy Safety, Treatment, Education, and Research) Act was signed into law, which categorized sesame as the ninth major food allergen.
This ever-increasing prevalence of allergy-inducing foods has presented lucrative opportunities for the food allergen testing industry in recent years since food processing business operators are placing a strong emphasis on ensuring transparency in their products’ ingredient lists. By testing for allergens in food products, organizations can accurately mention each ingredient, and thereby allow people with specific food allergies to avoid consuming them.
Several allergen detection methods are used in the food processing industry, including mass spectrometry, DNA-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) as well as ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), to name a few. The FDA, for instance, created a food allergen detection assay, called xMAP, designed to simultaneously identify 16 allergens, including sesame, within a single analysis, along with the ability to expand for the targeting of additional food allergens. Such industry advancements are improving the monitoring process for undeclared allergen presence in the food supply chain and enabling timely intervention upon detection.
Furthermore, initiatives, such as the Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labelling (VITAL), created and managed by the Allergen Bureau, are also shedding light on the importance of allergen testing in food production. The VITAL program is designed to support allergen management with the help of a scientific process for risk assessment, in order to comply with food safety systems like the HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point), with allergen analysis playing a key role in its application.
ELISA Gains Prominence as Ideal Tool for Food Allergen Testing
In life sciences, the detection and quantification of various antibodies or antigens in a cost-effective and timely manner is of utmost importance. Detection of select protein expression on a cell surface, identification of immune responses in individuals, or execution of quality control testing—all these assessments require a dedicated tool.
ELISA is one such tool proving to be instrumental for both diagnostics as well as research). Described as an immunological assay, ELISA is used commonly for the measurement of antibodies or antigens in biological samples, including glycoproteins or proteins.
While its utility continues to grow, ELISA-based testing has historically demonstrated excellent sensitivity in food allergen testing applications, in some cases down to ppm (parts per million). It has a distinct advantage over other allergen detection methods like PCR, owing to the ability to adapt to certain foods like milk and oils, where its counterparts tend to struggle. The FDA is one of the major promoters of ELISA for allergen testing in food production, involving the testing of food samples using two different ELISA kits, prior to confirming results.
Many major entities are also taking heed of the growing interest in the use of ELISA for food allergen diagnostics. A notable example of this is laboratory analyses test kits and systems supplier, Eurofins, which introduced its SENSISpec Soy Total protein ELISA kit in September 2020. The enzyme immunoassay, designed for quantitative identification of soy protein in swab and food samples, has been developed by Eurofins Immunolab to measure residues of processed protein in various food products, including instant meals, chocolate, baby food, ice cream, cereals, sausage, and cookies, among others.
In essence, food allergens continue to prevail as high-risk factors for the food production industry. Unlike other pathogens like bacteria, allergenic proteins are heat resistant and stable, and cannot easily be removed once present in the food supply chain. In this situation, diagnostic allergen testing, complete segregation of allergenic substances, and accurate food allergen labeling are emerging as the ideal courses of action for allergen management in the modern food production ecosystem, with advanced technologies like molecular-based food allergy diagnostics expected to take up a prominent role over the years ahead.